| Molecular Formula |
CuO
|
| Molecular Weight |
79.55
|
| Structure |
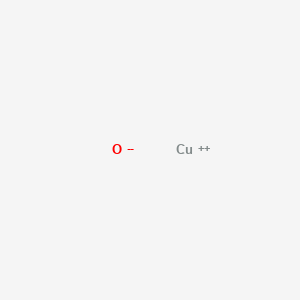
|
| State |
solid |
| Clearance |
No pharmacokinetic data available. |
| Volume of distribution |
Following exposure to cupric oxide aerosols containing 50-80 mg/m^3 in rats, particles were found in plasma 6 hours post-exposure and copper oxide was also observed in the proximal convoluted tubules of the kidney [L2422]. |
| Route of elimination |
Copper undergoes biliary excretion [L2422]. |
| Protein binding |
Once dissociated, copper is known to bind to serum albumin, ceruloplasmin, and other low-molecular weight complexes [L2422]. |
| Half life |
No pharmacokinetic data available. |
| Absorption |
Following oral administration, copper is mainly absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract from the stomach, duodenum, and jejunum. All other intakes of copper (inhalation and dermal) are insignificant in comparison to the oral route. The bioavailability of copper from cupric oxide depends on the solubilization of the oxide in the gastrointestinal tract [L2437]. According to studies on cattle and swine, copper oxide displays low absorption rate and high excretion rate [L2422]. In rats exposed to aerosols containing 50-80 mg/m^3, pulmonary uptake of copper oxide occurred [L2422]. |

