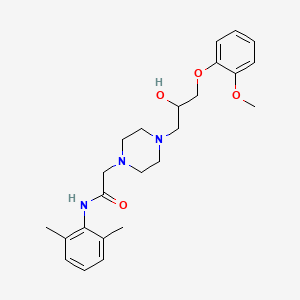
D1274 | ranolazine
C
C01EB18 Ranolazine
[C01EB] Other cardiac preparations
[C01E] OTHER CARDIAC PREPARATIONS
[C01] CARDIAC THERAPY
[C] Cardiovascular system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLYCOLYSIS | increase | 17 | ||||||
| FATTY ACID METABOLISM | 25μM | 24hr | T47D cells | quantifies the conversion of [9,10-3H(N)]-palmitic acid to 3H2O with diffusion | stimulate | Student’s two-tail t-test, where p < 0.05 | 273 | |
| MITOCHONDRIAL FATTY ACID BETA OXIDATION | decrease | 17 | ||||||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, somatic form, mitochondrial | 275 | |||||||
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
   |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 12 companies from 10 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 1 of 12 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 9 notification(s) provided by 11 of 12 companies with hazard statement code(s): H301 (27.27%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H302 (63.64%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H315 (36.36%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (27.27%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (36.36%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] H336 (18.18%): May cause drowsiness or dizziness [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Narcotic effects] H361 (27.27%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | > 600mg/kg (600mg/kg) | Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications. Vol. 50, Pg. 2289, 1985. | |
| women | TDLo | oral | 150mg/kg (150mg/kg) | Acta Medica Scandinavica. Vol. 218, Pg. 525, 1985. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 62mg/kg (62mg/kg) | United States Patent Document. Vol. #4252984, | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 1050mg/kg (1050mg/kg) | United States Patent Document. Vol. #4252984, | |
| dog | LD50 | intravenous | 60mg/kg (60mg/kg) | Pharmacological and Biochemical Properties of Drug Substances. Vol. 2, Pg. 186, 1979. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 3470mg/kg (3470mg/kg) | Drugs. International Journal of Current Therapeutics and Applied Pharmacology Reviews. Vol. 14, Pg. 321, 1977. | |
| women | TDLo | oral | 17mg/kg/17D-I (17mg/kg) | Annals of Internal Medicine. Vol. 108, Pg. 67, 1988. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | > 200mg/kg (200mg/kg) | Farmaco, Edizione Scientifica. Vol. 41, Pg. 80, 1986. | |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 71900ug/kg (71.9mg/kg) | Drugs. International Journal of Current Therapeutics and Applied Pharmacology Reviews. Vol. 14, Pg. 321, 1977. | |
| antianginal drug | assumed to be partial FAO inhibitors that targeted 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase (3-KAT), a component of the trifunctional protein (hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-KAT) | metabolic modifier |
| partial fatty-acid-oxidation inhibitor (pFOX inhibitor) |