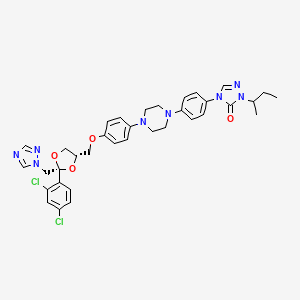
Drug
D1429 | itraconazole
J
J02AC02 Itraconazole
[J02AC] Triazole derivatives
[J02A] ANTIMYCOTICS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
[J02] ANTIMYCOTICS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
[J] Antiinfectives for systemic use
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIPID PEROXIDATION | 4mg/ml | Aspergillus fumigatus | lipid peroxidation using the thiobarbituric acid assay | induce | 304 | |||
| LIPID PEROXIDATION | 4mg/ml | Aspergillus fumigatus | mitochondrion-specific lipid peroxidation probe MitoPerOx | induce | 304 | |||
| ROS PRODUCTION | 4mg/ml | Aspergillus fumigatus | oxidant-sensing fluorescent probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate t | induce | 304 | |||