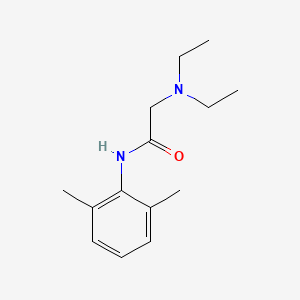
D0076 | Lidocaine
S
D
R
C
N
S02DA01 Lidocaine
[S02DA] Analgesics and anesthetics
[S02D] OTHER OTOLOGICALS
[S02] OTOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
S01HA07 Lidocaine
[S01HA] Local anesthetics
[S01H] LOCAL ANESTHETICS
[S01] OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
R02AD02 Lidocaine
[R02AD] Anesthetics, local
[R02A] THROAT PREPARATIONS
[R02] THROAT PREPARATIONS
[R] Respiratory system
N01BB52 Lidocaine, combinations
[N01BB] Amides
[N01B] ANESTHETICS, LOCAL
[N01] ANESTHETICS
[N] Nervous system
N01BB02 Lidocaine
[N01BB] Amides
[N01B] ANESTHETICS, LOCAL
[N01] ANESTHETICS
[N] Nervous system
D04AB01 Lidocaine
[D04AB] Anesthetics for topical use
[D04A] ANTIPRURITICS, INCL. ANTIHISTAMINES, ANESTHETICS, ETC.
[D04] ANTIPRURITICS, INCL. ANTIHISTAMINES, ANESTHETICS, ETC.
[D] Dermatological drugs
C05AD01 Lidocaine
[C05AD] Local anesthetics
[C05A] AGENTS FOR TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS AND ANAL FISSURES FOR TOPICAL USE
[C05] VASOPROTECTIVES
[C] Cardiovascular system
C01BB01 Lidocaine
[C01BB] Antiarrhythmics, class Ib
[C01B] ANTIARRHYTHMICS, CLASS I AND III
[C01] CARDIAC THERAPY
[C] Cardiovascular system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEPOLARIZATION | 197 | |||||||
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 339.5 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 188.2 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| OXYGEN CONSUMPTION RATE (OCR) | 300 μM | 2 minutes | human | HepG2 | Measurement of OCR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| ECAR | 300 μM | 2 minutes | human | HepG2 | Measurement of ECAR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| SWELLING | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Cytochrome c | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Warning |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 285 companies from 7 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 2 of 285 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 6 notification(s) provided by 283 of 285 companies with hazard statement code(s): H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
 |
Warning |
The GHS information provided by 1 company from 1 notification to the ECHA C&L Inventory. H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] |
P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
 |
Warning |
H302: Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] |
P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
  |
Danger |
H302: Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H362: May cause harm to breast-fed children [Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation] H370: Causes damage to organs [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure] H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] |
P201, P260, P261, P263, P264, P270, P272, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P307+P311, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P333+P313, P363, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| infant | TDLo | oral | 1632mg/kg/1W- (1632mg/kg) | Clinical Pediatrics Vol. 22, Pg. 190, 1983. | |
| infant | TDLo | intravenous | 10mg/kg (10mg/kg) | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 28, Pg. 101, 1990. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intramuscular | 177mg/kg (177mg/kg) | Drug Development Research. Vol. 21, Pg. 277, 1990. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 63mg/kg (63mg/kg) | Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. Vol. 274, Pg. 253, 1985. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 570mg/kg (570mg/kg) | Research Progress in Organic-Biological and Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 2, Pg. 299, 1970. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | intratracheal | 28mg/kg (28mg/kg) | Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. Vol. 200, Pg. 359, 1972. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 15mg/kg (15mg/kg) | Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. Vol. 14, Pg. 48T, 1962. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | intravenous | 25600ug/kg (25.6mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan Vol. 6, Pg. 879, 1982. | |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 7143ug/kg (7.143mg/kg) | cardiac: pulse rate increase without fall in bp | Chest. Vol. 61, Pg. 682, 1972. |
| dog | LDLo | intravenous | 65700ug/kg (65.7mg/kg) | Journal de Pharmacologie. Vol. 2, Pg. 240, 1971. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 163mg/kg (163mg/kg) | Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Vol. 103, Pg. 353, 1960. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 122mg/kg (122mg/kg) | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Vol. 111, Pg. 224, 1954. | |
| frog | LD50 | parenteral | 159mg/kg (159mg/kg) | Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. Vol. 289, Pg. 278, 1987. | |
| man | TDLo | implant | 5714ug/kg (5.714mg/kg) | behavioral: convulsions or effect on seizure threshold | Canadian Medical Association Journal. Vol. 137, Pg. 219, 1987. |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 220mg/kg (220mg/kg) | Research Progress in Organic-Biological and Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 2, Pg. 299, 1970. | |
| guinea pig | LD50 | intravenous | 24500ug/kg (24.5mg/kg) | Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. Vol. 113, Pg. 313, 1958. | |
| infant | TDLo | oral | 1600ug/kg/9H- (1.6mg/kg) | behavioral: convulsions or effect on seizure threshold | Annals of Emergency Medicine. Vol. 17, Pg. 725, 1988. |
| man | TDLo | intravenous | 9mg/kg/4H-C (9mg/kg) | cardiac: cardiomyopathy including infarction | Drug Intelligence and Clinical Pharmacy. Vol. 19, Pg. 669, 1985. |
| child | TDLo | intravenous | 60mg/kg/1H (60mg/kg) | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 24, Pg. 51, 1986. | |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 21mg/kg (21mg/kg) | Research Progress in Organic-Biological and Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 2, Pg. 299, 1970. | |
| (2,6-dimethylphenyl)carbamoylmethyl-diethyl-azanium | .alpha.-(Diethylamino)-2,6-acetoxylidide | .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-acetoxylidide |
| .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide | .alpha.-Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide | .omega.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide |
| 137-58-6 | 2', 2-(diethylamino)- | 2',6'-Acetoxylidide, 2-(diethylamino)- |
| 2-(Diethylamino)-2'',6''-acetoxylidide | 2-(Diethylamino)-2',6'-acetoxylidide | 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)ethanamide |
| 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide | 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide | 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide # |
| 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-acetamide | 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide | 4-12-00-02538 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| 6108-05-0 (MONOHYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE)) | 91484-71-8 | 98PI200987 |
| A18187 | AB00053581 | AB00053581-27 |
| AB00053581-28 | AB00053581_29 | AB00053581_30 |
| AB2000065 | AC-10282 | AKOS001026768 |
| ANW-42187 | ARONIS23855 | AS-13718 |
| Acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)- | Alphacaine | Alphacaine;Xylocaine;lignocaine |
| Anestacon | BBL005525 | BCP09081 |
| BDBM50017662 | BIDD:GT0342 | BPBio1_000197 |
| BRD-K52662033-001-02-6 | BRD-K52662033-003-05-5 | BRD-K52662033-003-14-7 |
| BRN 2215784 | BSPBio_000179 | BSPBio_001359 |
| BSPBio_003004 | Bio1_000379 | Bio1_000868 |
| Bio1_001357 | Bio2_000079 | Bio2_000559 |
| C07073 | C14H22N2O | CAS-137-58-6 |
| CAS-73-78-9 | CCG-100824 | CDS1_000283 |
| CHEBI:6456 | CHEMBL79 | CPD000058189 |
| CS-2070 | CTK3J2126 | Cappicaine |
| Certified Reference Material | Cito optadren | Cuivasil |
| D00358 | DB00281 | DSSTox_CID_25166 |
| DSSTox_GSID_45166 | DSSTox_RID_80716 | DTXSID1045166 |
| Dalcaine | Dentipatch | Dentipatch (TN) |
| Diethylaminoacet-2,6-xylidide | Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide | Dilocaine |
| DivK1c_000174 | DivK1c_001323 | Duncaine |
| EINECS 205-302-8 | ELA-Max | EMBOLEX |
| Epitope ID:116205 | Esracaine | FT-0082378 |
| FT-0600570 | GTPL2623 | Gravocain |
| HMS1791D21 | HMS1989D21 | HMS2051C21 |
| HMS2089E15 | HMS2235O14 | HMS3371J04 |
| HMS3393C21 | HMS3428O07 | HMS3651G09 |
| HMS548M19 | HSDB 3350 | HY-B0185 |
| IDI1_000174 | IDI1_033829 | Isicaina |
| Isicaine | J10173 | Jetocaine |
| K-4450 | KBio1_000174 | KBio2_000079 |
| KBio2_001598 | KBio2_002647 | KBio2_004166 |
| KBio2_005215 | KBio2_006734 | KBio3_000157 |
| KBio3_000158 | KBio3_002224 | KBioGR_000079 |
| KBioGR_000599 | KBioSS_000079 | KBioSS_001598 |
| KS-000046GY | L-Caine | L0156 |
| LIDOCAINE (73-58-6 (MONOHYDROCHLORIDE) | LIDOPEN | LQZ |
| LS-805 | Leostesin | Lida-Mantle |
| Lidaform HC (Salt/Mix) | Lidamantle HC (Salt/Mix) | Lidocaina |
| Lidocaina [INN-Spanish] | Lidocaine (Alphacaine) | Lidocaine (JP17/USP/INN) |
| Lidocaine (VAN) | Lidocaine 1.0 mg/ml in Methanol | Lidocaine Base |
| Lidocaine Hydrocarbonate | Lidocaine Monohydrochloride | Lidocaine [USAN:INN:JAN] |
| Lidocaine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | Lidocaine solution, 1.0 mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material | Lidocaine(Alphacaine) |
| Lidocaine, 97.5% | Lidocaine, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard | Lidocaine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard |
| Lidocaine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard | Lidocaine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard | Lidocaine, analytical standard |
| Lidocaine, powder | LidocaineHClH2O | Lidocainum |
| Lidocainum [INN-Latin] | Lidocaton | Lidoderm |
| Lidothesin (Salt/Mix) | Lignocaine | Lignocaine base |
| Lignocaine base 100 microg/mL in Methanol | Lignocainum | Lopac-L-5647 |
| Lopac0_000669 | M620 | MCULE-9294700940 |
| MFCD00026733 | MLS000069724 | MLS000758263 |
| MLS001074177 | MLS001423964 | Maricaine |
| Maybridge1_002571 | N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide | N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N(2),N(2)-diethylglycinamide |
| N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide | N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(diethylamino)acetamide | N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide |
| NC00074 | NCGC00015611-01 | NCGC00015611-02 |
| NCGC00015611-03 | NCGC00015611-04 | NCGC00015611-05 |
| NCGC00015611-06 | NCGC00015611-07 | NCGC00015611-08 |
| NCGC00015611-09 | NCGC00015611-10 | NCGC00015611-11 |
| NCGC00015611-12 | NCGC00015611-13 | NCGC00015611-14 |
| NCGC00015611-15 | NCGC00015611-16 | NCGC00015611-18 |
| NCGC00022176-05 | NCGC00022176-06 | NCGC00022176-07 |
| NCGC00022176-08 | NCGC00022176-09 | NINDS_000174 |
| NNJVILVZKWQKPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | NSC 40030 | NSC-40030 |
| NSC40030 | Neosporin Plus (Salt/Mix) | N~1~-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide |
| Octocaine | Opera_ID_385 | Prestwick0_000050 |
| Prestwick1_000050 | Prestwick2_000050 | Prestwick3_000050 |
| Q216935 | Qualigens | RTR-031283 |
| Remicaine | Rucaina | SAM001247018 |
| SB19118 | SBB080556 | SBI-0050648.P004 |
| SC-19460 | SCHEMBL15689 | SCHEMBL17967359 |
| SMR000058189 | SPBio_001525 | SPBio_002100 |
| ST023341 | STK552033 | SW196598-4 |
| Solcain | Spectrum2_001343 | Spectrum3_001392 |
| Spectrum4_000070 | Spectrum5_001549 | Spectrum_001118 |
| TR-031283 | Tox21_110183 | Tox21_110183_1 |
| UNII-98PI200987 | Versatis | W-108233 |
| WLN: 2N2 & 1VMR B1 F1 | Xilina | Xilocaina |
| Xilocaina [Italian] | Xllina | Xycaine |
| Xylestesin | Xylesthesin | Xyline |
| Xylocain | Xylocaine | Xylocaine (TN) |
| Xylocaine CO2 | Xylocitin | Xyloneural (Salt/Mix) |
| Xyloneural (free base) | Xylotox | Z55135799 |
| ZINC20237 | ZTlido | Zingo (Salt/Mix) |
| Ztilido | alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide | alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide [Italian] |
| alpha-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide | lidocaine | s1357 |
| DrugBank Name | Lidocaine |
| DrugBank | DB00281 |
| CAS Number | 137-58-6, 34941-90-7, 73-78-9, 91484-71-8 |
| PubChem Compound | 3676 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C07073 |
| KEGG Drug | D00358 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46505060 |
| ChEBI | 6456 |
| PharmGKB | PA450226 |
| ChemSpider | 3548 |
| BindingDB | 50017662.0 |
| TTD | DAP000121 |
| Wikipedia | Lidocaine |
| HET | LQZ |
| DPD | 10225|9471 |