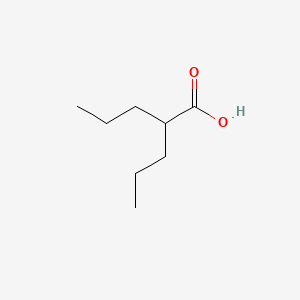
D0126 | Valproic Acid
N
N03AG01 Valproic acid
[N03AG] Fatty acid derivatives
[N03A] ANTIEPILEPTICS
[N03] ANTIEPILEPTICS
[N] Nervous system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 267.2 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 44.9 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| MITOCHONDRIAL FATTY ACID BETA OXIDATION | affect | 227 | ||||||
| TRANSPORT OF PYRUVATE | 0.5–2 mM | 3min | rat | inverted submitochondrial vesicles (ISMV) from rat liver isolated mitochondria | The rate of the radiolabeled substrate [1-14C]-pyruvate uptake by ISMV was measured in the presence or absence of an inwardly directed proton gradient. | inhibitor | 279 | |
| SWELLING | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| ROS PRODUCTION | increase | 197 | ||||||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | 44.9 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| carnitine palmitoyltransferases I | inhibit | 227 | ||||||
| Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1 | 0.5–2 mM | 3min | rat | inverted submitochondrial vesicles (ISMV) from rat liver isolated mitochondria | The rate of the radiolabeled substrate [1-14C]-pyruvate uptake by ISMV was measured in the presence or absence of an inwardly directed proton gradient. | inhibit | 279 | |
| Cytochrome c | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
   |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 280 companies from 17 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H315 (96.43%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H318 (60.71%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H319 (35.71%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (14.29%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] H360 (84.64%): May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
  |
Danger |
H302: Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Narcotic effects] H360: May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity] H362: May cause harm to breast-fed children [Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation] H370: Causes damage to organs [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure] H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] |
P201, P202, P260, P261, P263, P264, P270, P271, P281, P301+P312, P304+P340, P307+P311, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P330, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| (S)-2-propyl-4-pentanoate | (n-C3H7)2CHCOOH | 2 -propylpentanoic acid |
| 2 PP (base) | 2,2-di-n-propylacetic acid | 2-PROPYL-PENTANOIC ACID |
| 2-Propylpentanoic acid | 2-Propylpentanoic acid sodium salt | 2-Propylpentanoic acid, 99% |
| 2-PropylpentanoicAcid | 2-Propylvaleric acid | 2-n-Propyl-n-valeric acid |
| 2-propyl-Pentanoate | 33433-82-8 | 4-Heptanecarboxylic acid |
| 614OI1Z5WI | 6400-EP1441224A2 | 6400-EP2272537A2 |
| 6400-EP2272827A1 | 6400-EP2275420A1 | 6400-EP2280008A2 |
| 6400-EP2298764A1 | 6400-EP2298765A1 | 6400-EP2308867A2 |
| 6400-EP2308870A2 | 6400-EP2311494A1 | 6400-EP2311840A1 |
| 6400-EP2314585A1 | 6400-EP2374790A1 | 791-EP2306789A1 |
| 99-66-1 | A-44090 | A19450 |
| AB0009719 | AB00698315-06 | ACMC-209sdq |
| ACT05281 | AI3-10500 | AK128830 |
| AKOS009156895 | ANW-41052 | APO-divalproex |
| AS-11354 | Abbott 44090 | Acetic acid, dipropyl- |
| Acide valproique | Acide valproique [INN-French] | Acido valproico |
| Acido valproico [INN-Spanish] | Acidum valproicum | Acidum valproicum [INN-Latin] |
| Alti-Valproic | Apo-valproic | Apo-valproic syrup |
| Avugane | BDBM50003616 | BIDD:GT0858 |
| BRN 1750447 | Baceca | C07185 |
| CAS-99-66-1 | CCG-221127 | CHEBI:39867 |
| CHEMBL109 | CPD000499581 | CS-1765 |
| CTK3J3389 | Certified Reference Material | Convulex |
| Convulex (Salt/Mix) | Convulsofin | D00399 |
| DB00313 | DOM-divalproex | DOM-valproic acid E.C. |
| DSSTox_CID_3733 | DSSTox_GSID_23733 | DSSTox_RID_77171 |
| DTXSID6023733 | Depacon (Salt/Mix) | Depakene |
| Depakene (TN) | Depakin | Depakin chrono |
| Depakine | Depakine chrono | Depakote (TM) |
| Depakote CP | Deproic | Di-n-propylacetic acid |
| Di-n-propylessigsaeure | Di-n-propylessigsaure | Di-n-propylessigsaure [German] |
| Dipropyl Acetate | Dipropylacetate | Dipropylacetic acid |
| DivK1c_000273 | Divalproex (Salt/Mix) | Dom-Valproic |
| Dom-valproate | Dom-valproic acid | Dom-valproic acid syrup |
| EC 202-777-3 | EINECS 202-777-3 | Epical (TM) |
| Epiject I.V. | Epilim | Epilim (Salt/Mix) |
| Epival er | Erganyl | Ergenyl |
| Eurekene (Salt/Mix) | F2191-0115 | FT-0609289 |
| G2M-777 | GTPL7009 | Gen-divalproex |
| HMS2089J06 | HMS2231E06 | HMS3259C18 |
| HMS3370C21 | HMS3715B15 | HSDB 3582 |
| HY-10585 | Heptane-4-carboxylic acid | InChI=1/C8H16O2/c1-3-5-7(6-4-2)8(9)10/h7H,3-6H2,1-2H3,(H,9,10) |
| KBio1_000273 | KBio2_001001 | KBio2_002277 |
| KBio2_003569 | KBio2_004845 | KBio2_006137 |
| KBio2_007413 | KBio3_002626 | KBio3_002757 |
| KBioGR_000871 | KBioGR_002277 | KBioSS_001001 |
| KBioSS_002278 | KS-00000CCR | KSC493G8T |
| Kyselina 2-propylvalerova | Kyselina 2-propylvalerova [Czech] | LMFA01020291 |
| LS-161170 | LS-2068 | MCULE-7136317196 |
| MFCD00002672 | MLS001076682 | MLS001335927 |
| MLS001335928 | MLS002415770 | Med Valproic |
| Mylproin | Myproic Acid | NC00584 |
| NCGC00091149-01 | NCGC00091149-02 | NCGC00091149-03 |
| NCGC00091149-04 | NCGC00091149-05 | NCGC00091149-06 |
| NCGC00091149-08 | NCGC00091149-09 | NCGC00162288-07 |
| NCGC00254365-01 | NCGC00259512-01 | NIJJYAXOARWZEE-UHFFFAOYSA- |
| NIJJYAXOARWZEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | NINDS_000273 | NSC 93819 |
| NSC-93819 | NSC93819 | Novo-Valproic |
| Novo-Valproic - ECC | Novo-divalproex | Novo-valproic soft gel cap |
| Nu-Valproic | P0823 | PHL-valproate |
| PHL-valproic acid | PHL-valproic acid E.C. | PMS-Divalproex |
| PMS-Valproic Acid | PMS-valproate | PMS-valproic acid E.C. |
| Penta-Valproic | Pentanoic acid, 2-propyl- | Propylvaleric acid |
| Q-200321 | Q240642 | RTR-031980 |
| Ratio-Valproic - ECC | S(-)-4-En-valproate | S-2-n-Propyl-4-pentenoate |
| SAM002564230 | SBB065764 | SBI-0050864.P003 |
| SCHEMBL2275 | SMR000499581 | SPBio_000912 |
| SR-01000075242-7 | STL445581 | Sandoz valproic |
| Savicol | Sodium valproate | Spectrum2_000946 |
| Spectrum3_001733 | Spectrum4_000376 | Spectrum_000521 |
| Stavzor | Stavzor | TR-031980 |
| TRA0085608 | Tox21_111091 | Tox21_111091_1 |
| Tox21_201963 | Tox21_300603 | UNII-614OI1Z5WI |
| VALPROIC ACID | VPA | Valdisoval (Salt/Mix) |
| Valeric acid, 2-propyl- | Valparin (Salt/Mix) | Valproate |
| Valproic Acid 1.0 mg/ml in Methanol | Valproic Acid, Sodium Salt (2:1) | Valproic acid (USP) |
| Valproic acid USP | Valproic acid [USAN:BAN:INN] | Valproic acid [USAN:INN:BAN] |
| Valproic acid [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | Valproic acid for system suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Valproic acid solution, 1.0 mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material |
| Valproic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Valproic acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard | Valproic acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard |
| Valproinsaeure | Valproinsaure | Vupral |
| WLN: QVY3 & 3 | Z1511532065 | ZINC3008621 |
| di-n-propyl acetic acid | divalproex | n-DPA |
| n-Dipropylacetic acid |
| DrugBank Name | Valproic Acid |
| DrugBank | DB00313 |
| CAS Number | 1069-66-5, 362049-65-8, 76584-70-8, 99-66-1, 99-67-2 |
| PubChem Compound | 3121 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C07185 |
| KEGG Drug | D00399 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46505925 |
| ChEBI | 39867 |
| PharmGKB | PA451846 |
| ChemSpider | 3009 |
| BindingDB | 50003616.0 |
| TTD | DNC001659 |
| Wikipedia | Valproic_Acid |
| HET | 2PP |
| DPD | 2115 |