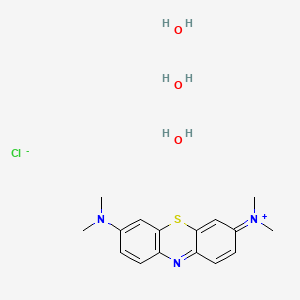
D0997 | methylene blue trihydrate
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 1.31±0.79 | human | qHTS-HepG2 | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 4.82 | human | HepG2 | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 7.29±7.49 | rat | hepatocytes | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
  |
Warning |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 76 companies from 7 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 7 of 76 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 6 notification(s) provided by 69 of 76 companies with hazard statement code(s): H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H315 (65.22%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (94.2%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (62.32%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] H373 (28.99%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P314, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| guinea pig | LDLo | subcutaneous | 300mg/kg (300mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1366, 1935. | |
| dog | LDLo | intravenous | 50mg/kg (50mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1366, 1935. | |
| domestic animals - goat/sheep | LD50 | intravenous | 42300ug/kg (42.3mg/kg) | Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Vol. 7, Pg. 225, 1984. | |
| dog | LDLo | oral | 500mg/kg (500mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1366, 1935. | |
| infant | TDLo | unreported | 15mg/kg (15mg/kg) | "Toxicology of Drugs and Chemicals," Deichmann, W.B., New York, Academic Press, Inc., 1969Vol. -, Pg. 390, 1969. | |
| monkey | LDLo | intravenous | 10mg/kg (10mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1366, 1935. | |
| rabbit | LDLo | oral | 1gm/kg (1000mg/kg) | "Abdernalden's Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden." Vol. 4, Pg. 1366, 1935. | |
| man | TDLo | subcutaneous | 28uL/kg (0.028mL/kg) | skin and appendages (skin): "dermatitis, other: after systemic exposure" | British Journal of Clinical Practice. Vol. 28, Pg. 289, 1974. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 150mg/kg (150mg/kg) | National Technical Information Service. Vol. AD691-490, | |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 1250mg/kg (1250mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 18, Pg. 676, 1968. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 77mg/kg (77mg/kg) | Cesko-Slovenska Farmacie. Vol. 12, Pg. 94, 1963. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 1180mg/kg (1180mg/kg) | "Prehled Prumyslove Toxikologie; Organicke Latky," Marhold, J., Prague, Czechoslovakia, Avicenum, 1986Vol. -, Pg. 1334, 1986. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 190mg/kg (190mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan Vol. -, Pg. 1185, 1990. | |
| cat | LDLo | intravenous | 41mg/kg (41mg/kg) | Annals of Internal Medicine. Vol. 7, Pg. 738, 1933. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 3500mg/kg (3500mg/kg) | Cesko-Slovenska Farmacie. Vol. 12, Pg. 94, 1963. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 180mg/kg (180mg/kg) | Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archiv fuer Experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie. Vol. 204, Pg. 288, 1947. | |
| 3,7-Bis(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-5-ium chloride trihydrate | 61-73-4 (anhydrous) | 6337AF |
| 7220-79-3 | AC-8349 | AKOS015915395 |
| Basic Blue 9 trihydrate | C.I. 52015 | C.I. Basic Blue 9 trihydrate |
| C.I. Basic Blue 9, trihydrate | C.I. Basic Blue 9, trihydrate (8CI) | C16H18ClN3S |
| C16H18N3S.Cl.3H2O | C16H20N3S.3H2O.Cl | CAS-7220-79-3 |
| CCRIS 9312 | CHEMBL550495 | CI 52015 |
| D02312 | DSSTox_CID_5600 | DSSTox_GSID_25600 |
| DSSTox_RID_77848 | DTXSID0025600 | FT-0628873 |
| GT0735 | KS-00000YCE | LS-1619 |
| MFCD00012111 | MFCD00150008 | Methylene Blue [USAN] |
| Methylene Blue trihydrate | Methylene Blue trihydrate (C.I. 52015) | Methylene Blue trihydrate, 95%, pure |
| Methylene blue (USP) | Methylene blue [USP] | Methylthionine HCl |
| Methylthionine chloride | Methylthioninium chloride proveblue (TN) | NCGC00091924-01 |
| NCGC00260074-01 | NSC-215213 | NSC-617593 |
| Phenothiazin-5-ium, 3,7-bis(dimethylamino)-, chloride, trihydrate | ST50406156 | T42P99266K |
| Tox21_202525 | Trx0014 | UNII-T42P99266K |
| [7-(dimethylamino)benzo[e]benzo[3,4-b]1,4-thiazin-3-yl]dimethylamine, hydrate, hydrate, hydrate, chloride; | [7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium chloride |
| CAS Number | 122965-43-9, 61-73-4, 7220-79-3, 75007-33-9 |
| PubChem Compound | 104827 |