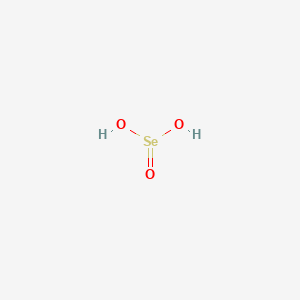
D1089 | selenious acid
A
A12CE02 Sodium selenite
[A12CE] Selenium
[A12C] OTHER MINERAL SUPPLEMENTS
[A12] MINERAL SUPPLEMENTS
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 15.97±22.77 | human | qHTS-HepG2 | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | human | HepG2 | MMP assay | Negative | IC50 | 163 | ||
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 44.11±26.85 | rat | hepatocytes | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
   |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 204 companies from 15 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H331 (99.51%): Toxic if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation] H373 (42.16%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H400 (98.53%): Very toxic to aquatic life [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard] H410 (99.51%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+P310, P304+P340, P311, P314, P321, P330, P391, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
  |
Danger |
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage [Danger Skin corrosion/irritation] H318: Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H370: Causes damage to organs [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure] H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] |
P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P307+P311, P310, P314, P321, P363, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
  |
Danger |
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage [Danger Skin corrosion/irritation] H318: Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H372: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H373: Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] |
P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P314, P321, P363, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rat | LDLo | intraperitoneal | 10mg/kg (10mg/kg) | National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Chemical-Biological Coordination Center, Review. Vol. 5, Pg. 28, 1953. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 11mg/kg (11mg/kg) | U.S. Army Armament Research & Development Command, Chemical Systems Laboratory, NIOSH Exchange Chemicals. Vol. NX#05656, | |
| rat | LDLo | oral | 25mg/kg (25mg/kg) | National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Chemical-Biological Coordination Center, Review. Vol. 5, Pg. 28, 1953. | |
| 7783-00-8 | AKOS015960374 | CAS-7783-00-8 |
| CCG-35433 | CCRIS 5530 | CHEBI:26642 |
| CHEMBL2009089 | CTK2H8628 | D05814 |
| DB11127 | DSSTox_CID_4300 | DSSTox_GSID_24300 |
| DSSTox_RID_77360 | DTXSID9024300 | EC 231-974-7 |
| EINECS 231-974-7 | F6A27P4Q4R | HSDB 6065 |
| KS-0000193L | LS-144800 | MCAHWIHFGHIESP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MFCD00011331 | Monohydrated selenium dioxide | NCGC00248596-01 |
| NCGC00257961-01 | NCI60_003085 | NCIMech_000026 |
| Q413722; | SELENIOUS ACID | Selenious acid (H2SeO3) |
| Selenious acid (USP) | Selenious acid [USP] | Selenious acid, 98% |
| Selenious acid, 99.999%, (trace metal basis) | Selenite (SeO32-) | Selenite ion (SeO32-) |
| Selenite ion(2-) | Selenium dioxide, monohydrated | Selenium, Reference Standard Solution |
| Selenous acid | Selenous acid, 98% | Selenous acid, 99.999% trace metals basis |
| Selenous acid, Puratronic? | Selenous acid, p.a., 95.0% | TR-024855 |
| Tox21_200407 | UN-3283 | UNII-F6A27P4Q4R |
| VZ36877 | [SeO(OH)2] | dihydroxidooxidoselenium |
| selenige Saeure | selenious acid,selenous acid,monohydrated selenium dioxide |