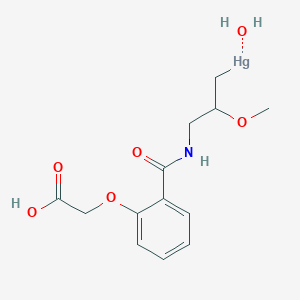
D1328 | Mersalyl
C
C03BC01 Mersalyl
[C03BC] Mercurial diuretics
[C03B] LOW-CEILING DIURETICS, EXCL. THIAZIDES
[C03] DIURETICS
[C] Cardiovascular system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROTON CONDUCTIVITY | 130 μM | bovine | heart MF0, proton conductivity | affect | 70% inhibition | 170 | ||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fo subunits | 130 μM | bovine | heart MF0, proton conductivity | inhibitor | 70% inhibition | 170 | ||
| Phosphate carrier protein, mitochondrial | inhibitor | 230 | ||||||
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
   |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 38 companies from 1 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H300 (100%): Fatal if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H310 (100%): Fatal in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal] H330 (100%): Fatal if inhaled [Danger Acute toxicity, inhalation] H373 (100%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H400 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard] H410 (100%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P350, P304+P340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| (3-(2-(carboxymethoxy)benzamido)-2-methoxypropyl)(hydroxy)mercury | 486-67-9 | ACM486679 |
| API0003303 | C-33804 | C11336 |
| CAS-486-67-9 | CHEBI:6771 | DB09338 |
| DSSTox_CID_26902 | DSSTox_GSID_46902 | DSSTox_RID_82001 |
| DTXSID3046902 | GTPL5331 | Mercurate(1-), [3-[[2-(carboxylatomethoxy)benzoyl]amino]-2-methoxypropyl]hydroxy-, hydrogen |
| Mersal | Mersalyl | Mersalyl acid |
| Mersalyl acid, analytical standard | NCGC00181320-01 | Q424871 |
| SCHEMBL993248 | Tox21_112788 |