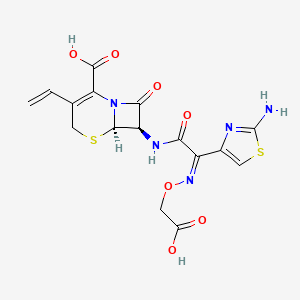
D1391 | Cefixime
J
J01DD08 Cefixime
[J01DD] Third-generation cephalosporins
[J01D] OTHER BETA-LACTAM ANTIBACTERIALS
[J01] ANTIBACTERIALS FOR SYSTEMIC USE
[J] Antiinfectives for systemic use
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | > 400 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 41.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 216.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| SWELLING | > 400 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 41.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | 216.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Cytochrome c | > 400 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
  |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 56 companies from 6 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 1 of 56 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 5 notification(s) provided by 55 of 56 companies with hazard statement code(s): H315 (23.64%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H317 (100%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H319 (23.64%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H334 (27.27%): May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled [Danger Sensitization, respiratory] H335 (23.64%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P285, P302+P352, P304+P340, P304+P341, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P342+P311, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rat | LD50 | oral | > 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: "hypermotility, diarrhea" | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | > 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | behavioral: somnolence (general depressed activity) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 6990mg/kg (6990mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | > 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: "hypermotility, diarrhea" | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. |
| dog | LD50 | oral | > 600mg/kg (600mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: "hypermotility, diarrhea" | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. |
| dog | LD50 | intravenous | > 3200mg/kg (3200mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 4420mg/kg (4420mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | > 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | behavioral: somnolence (general depressed activity) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 20, Pg. 3509, 1986. |