Drug
D0021 | Cerivastatin
C
C10AA06 Cerivastatin
[C10AA] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
[C10A] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPENING OF PERMEABILITY TRANSITION PORE (PTP) | 10 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Decrease | MEC | 306 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 50 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Decrease | MEC | 306 |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 100uM | C2C12 myoblasts | measured ubiquinol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase activity in broken C2C12 mitochondria after acute statin exposure at a fixed concentration for all compounds | decrease | 180 | |||
| ROS PRODUCTION | 5 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Increase | MEC | 306 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | 100uM | C2C12 myoblasts | measured ubiquinol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase activity in broken C2C12 mitochondria after acute statin exposure at a fixed concentration for all compounds | inhibitor | 180 | |||
| Reactive oxygen species | 5 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | increase | MEC | 306 |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 221mg/kg (221mg/kg) | Gekkan Yakuji. Pharmaceuticals Monthly. Vol. 42, Pg. 402, 2000. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 416mg/kg (416mg/kg) | Gekkan Yakuji. Pharmaceuticals Monthly. Vol. 42, Pg. 402, 2000. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 416mg/kg (416mg/kg) | Gekkan Yakuji. Pharmaceuticals Monthly. Vol. 42, Pg. 402, 2000. | |
| dog | LDLo | oral | 32mg/kg (32mg/kg) | Gekkan Yakuji. Pharmaceuticals Monthly. Vol. 42, Pg. 402, 2000. | |
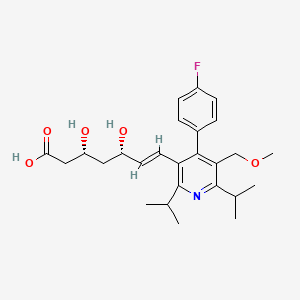
| (3R,5S,6E)-7-(4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)-3-pyridinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid | (3R,5S,6E)-7-(4-(p-Fluorophenyl)-2,6-diisopropyl-5-(methoxymethyl)-3-pyridyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid | (3R,5S,6E)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-bis(propan-2-yl)pyridin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid |
| (3R,5S,6E)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-di(propan-2-yl)pyridin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid | (3R,5S,6E)-7-{4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)-5-[(methyloxy)methyl]pyridin-3-yl}-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid | (3R,5S,E)-7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2,6-diisopropyl-5-(methoxymethyl)pyridin-3-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid |
| (E,3R,5S)-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-di(propan-2-yl)pyridin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid | 145599-86-6 | 599C866 |
| 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)-3-pyridinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-, (3R,5S,6E)- | 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-(4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2,6-bis(1-methylethyl)-3-pyridinyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-, (S-(R*,S*-(E)))- | AB01275453-01 |
| AM91H2KS67 | API0000459 | BDBM18376 |
| BIDD:GT0367 | BRD-K81169441-236-04-1 | C07966 |
| CHEBI:3558 | CHEBI:94755 | CHEMBL1477 |
| CS-0105635 | Cerivastatin (INN) | Cerivastatin [INN:BAN] |
| Cervastatin | D07661 | DB00439 |
| DTXSID9022786 | GTPL2950 | HMS2089B11 |
| HSDB 7357 | HY-129458 | LS-183259 |
| LS-187162 | Q423439 | SCHEMBL16346 |
| SCHEMBL16347 | SEERZIQQUAZTOL-ANMDKAQQSA-N | SR-01000763520 |
| SR-01000763520-3 | UNII-AM91H2KS67 | ZINC11330186 |
| [S-[R*,S*-(E)]]-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methoxymethyl)-2,6bis(1-methylethyl)-3-pyridinyl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoate | cerivastatin | cerivastatin acid |
| DrugBank Name | Cerivastatin |
| DrugBank | DB00439 |
| CAS Number | 143201-11-0, 145599-86-6 |
| PubChem Compound | 446156 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C07966 |
| KEGG Drug | D07661 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46505877 |
| ChEBI | 3558 |
| PharmGKB | PA448897 |
| ChemSpider | 393588 |
| BindingDB | 18376.0 |
| TTD | DNC000403 |
| Wikipedia | Cerivastatin |
| HET | 116 |
| DPD | 11747 |
1. Dykens et al. (2014)