D0069 | Indomethacin
S
M
C
S01CC02 Indometacin and antiinfectives
[S01CC] Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids and antiinfectives in combination
[S01C] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS AND ANTIINFECTIVES IN COMBINATION
[S01] OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
S01BC01 Indometacin
[S01BC] Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids
[S01B] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS
[S01] OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
M02AA23 Indometacin
[M02AA] Antiinflammatory preparations, non-steroids for topical use
[M02A] TOPICAL PRODUCTS FOR JOINT AND MUSCULAR PAIN
[M02] TOPICAL PRODUCTS FOR JOINT AND MUSCULAR PAIN
[M] Musculoskeletal system
M01AB51 Indometacin, combinations
[M01AB] Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
[M01A] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS, NON-STEROIDS
[M01] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS
[M] Musculoskeletal system
M01AB01 Indometacin
[M01AB] Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
[M01A] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS, NON-STEROIDS
[M01] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS
[M] Musculoskeletal system
C01EB03 Indometacin
[C01EB] Other cardiac preparations
[C01E] OTHER CARDIAC PREPARATIONS
[C01] CARDIAC THERAPY
[C] Cardiovascular system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNCOUPLING | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | increase | 65 | ||||
| UNCOUPLING | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | measurements of mitochondrial respiration; RST inhibition assay, RST uncoupling assay; IC 50ratio of glucose/galactose assay | Negative | 53 | |||
| UNCOUPLING | 197 | |||||||
| UNCOUPLING | 197 | |||||||
| UNCOUPLING | rat | heart | 197 | |||||
| PROTONOPHORIC UNCOUPLING | 278 | |||||||
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 443.2 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 25.2 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | decrease | 65 | ||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | measurements of mitochondrial respiration; RST inhibition assay, RST uncoupling assay; IC 50ratio of glucose/galactose assay | Negative | 53 | |||
| SWELLING | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| MEGAMITOCHONDRIA | 0.3-0.5 mM | 22 h | primary culture rat hep-atocytes, RL-34,COS-1, IAR-20 | induce | 292 | |||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 25.2 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | inhibitor | 162 | ||||||
| Cytochrome c | > 200 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
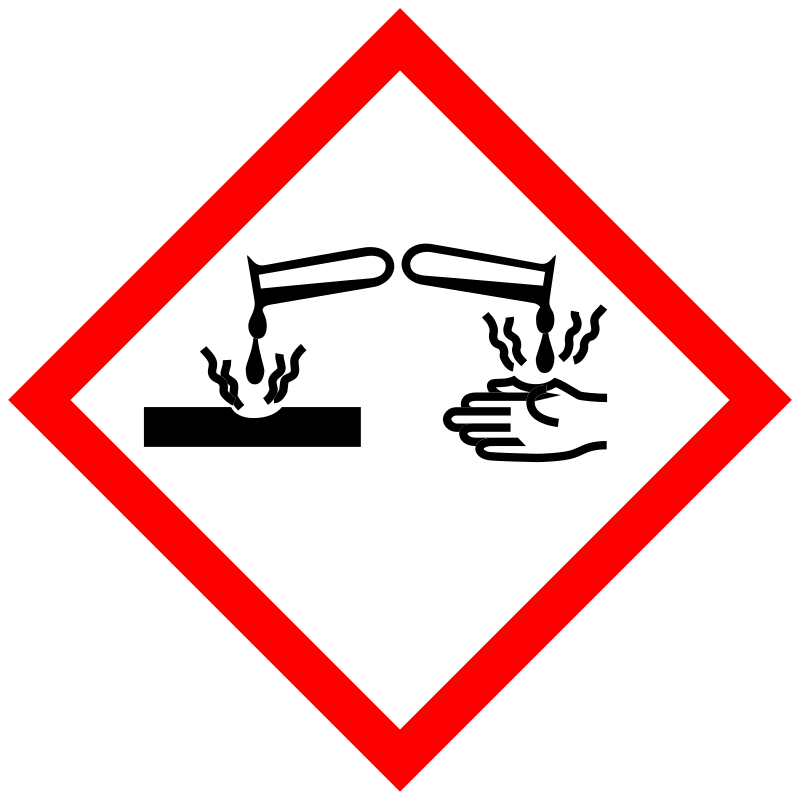    |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 159 companies from 19 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H300 (77.36%): Fatal if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H301 (22.64%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H317 (11.95%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H318 (22.01%): Causes serious eye damage [Danger Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (22.01%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] H336 (22.01%): May cause drowsiness or dizziness [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Narcotic effects] H360 (12.58%): May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity] H373 (22.01%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H413 (22.01%): May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P314, P321, P330, P333+P313, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
 |
Danger |
H300: Fatal if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] |
P264, P270, P301+P310, P321, P330, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 18300ug/kg (18.3mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| cat | LDLo | intravenous | 20200ug/kg (20.2mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 33, Pg. 726, 1983. | |
| man | TDLo | rectal | 2586mg/kg/3.5 (2586mg/kg) | sense organs and special senses: "retinal changes (pigmentary depositions, retinitis, other): eye" | American Journal of Ophthalmology. Vol. 73, Pg. 846, 1972. |
| human | TDLo | oral | 113mg/kg/8W-I (113mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 33, Pg. 636, 1983. | |
| man | TDLo | oral | 714ug/kg (0.714mg/kg) | Allergy. Vol. 54, Pg. 90, 1999. | |
| man | TDLo | unreported | 499mg/kg/87W- (499mg/kg) | Arthritis and Rheumatism. Vol. 20, Pg. 917, 1977. | |
| man | TDLo | oral | 22500ug/kg/3W (22.5mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: ulceration or bleeding from large intestine | Annals of Pharmacotherpy. Vol. 29, Pg. 883, 1994. |
| mammal (species unspecified) | LD50 | oral | 8mg/kg (8mg/kg) | Indian Journal of Medical Research. Vol. 81, Pg. 621, 1985. | |
| guinea pig | LD50 | oral | 100mg/kg (100mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 2, Pg. 70, 1968. | |
| infant | TDLo | oral | 400ug/kg/2D-I (0.4mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: necrotic ghanges | Journal of Pediatrics. Vol. 107, Pg. 484, 1985. |
| women | TDLo | oral | 2098ug/kg/1D- (2.098mg/kg) | Southern Medical Journal. Vol. 78, Pg. 1390, 1985. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 2420ug/kg (2.42mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: ulceration or bleeding from stomach | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 25, Pg. 1526, 1975. |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 13mg/kg (13mg/kg) | Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. Vol. 38, Pg. 127, 1976. | |
| infant | TDLo | intravenous | 200ug/kg (0.2mg/kg) | blood: hemorrhage | Journal of Pediatrics. Vol. 107, Pg. 312, 1985. |
| man | LDLo | oral | 15mg/kg/2W-I (15mg/kg) | blood: aplastic anemia | Israel Journal of Medical Sciences. Vol. 17, Pg. 433, 1981. |
| man | TDLo | multiple routes | 3557mg/kg/5Y- (3557mg/kg) | sense organs and special senses: "retinal changes (pigmentary depositions, retinitis, other): eye" | American Journal of Ophthalmology. Vol. 73, Pg. 846, 1972. |
| rat | LD50 | rectal | 31900ug/kg (31.9mg/kg) | Yakuri to Chiryo. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Vol. 14, Pg. 2259, 1986. | |
| dog | LD50 | oral | 160mg/kg (160mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 2, Pg. 70, 1968. | |
| rat | LD50 | intravenous | 21mg/kg (21mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 31, Pg. 655, 1981. | |
| women | TDLo | oral | 10mg/kg (10mg/kg) | behavioral: coma | Japanese Journal of Toxicology. Vol. 12, Pg. 337, 1999. |
| man | TDLo | oral | 4286ug/kg/2D- (4.286mg/kg) | skin and appendages (skin): "dermatitis, other: after systemic exposure" | Postgraduate Medical Journal. Vol. 72, Pg. 186, 1996. |
| dog | LD50 | intravenous | 100mg/kg (100mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| rabbit | LD50 | oral | 135mg/kg (135mg/kg) | Drugs in Japan Vol. 6, Pg. 90, 1982. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 11841ug/kg (11.841mg/kg) | German Offenlegungsschrift Patent Document. Vol. #3005827, | |
| guinea pig | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 143mg/kg (143mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 10mg/kg (10mg/kg) | Archivos de Farmacologia y Toxicologia. Vol. 8, Pg. 201, 1982. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 12mg/kg (12mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 2, Pg. 70, 1968. | |
| hamster | LD50 | oral | 81mg/kg (81mg/kg) | Archives of Toxicology, Supplement. Vol. 7, Pg. 365, 1984. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intramuscular | 18200ug/kg (18.2mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| rat | LD | skin | > 250mg/kg (250mg/kg) | Yakuri to Chiryo. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Vol. 14, Pg. 3185, 1986. | |
| guinea pig | LD50 | intravenous | 180mg/kg (180mg/kg) | Journal de Pharmacologie. Vol. 2, Pg. 259, 1971. | |
| rat | LD50 | intramuscular | 26300ug/kg (26.3mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| man | TDLo | oral | 22500ug/kg/3W (22.5mg/kg) | British Medical Journal. Vol. 3, Pg. 155, 1967. | |
| guinea pig | LD | skin | > 100mg/kg (100mg/kg) | behavioral: excitement | Yakuri to Chiryo. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. Vol. 14, Pg. 3185, 1986. |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 30mg/kg (30mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 19, Pg. 1198, 1969. | |
| cat | LD50 | oral | 320mg/kg (320mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| (1-p-Chlorobenzoyl-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl)acetic acid | .alpha.-(1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolyl)acetic acid | 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxyindole-3-acetic acid |
| 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid | 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic acid & MAP-30 | 1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indoleacetic acid |
| 1-(4-chloro-benzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolyl-acetic acid | 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid | 1-(p-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-essigsaeure |
| 1-(p-Chlorbenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-essigsaeure [German] | 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methoxy-3-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetic Acid | 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indole-acetic acid |
| 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxyindole-3-acetic acid | 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-acetic acid | 1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid |
| 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indoleacetic acid | 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolylacetic acid | 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indol acetic acid |
| 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indoleacetic acid | 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-3-indolylacetic acid | 1-p-Cloro-benzoil-5-metoxi-2-metilindol-3-acido acetico |
| 1-p-Cloro-benzoil-5-metoxi-2-metilindol-3-acido acetico [Spanish] | 1-p-chlorobenzoyl-2-methyl-5-methoxyindol-3-acetic acid | 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- |
| 1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- (9CI) | 1z9h | 2-(1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid |
| 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid | 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-indol-3-yl]acetic acid | 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetic acid |
| 2-{1-((4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid | 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2 methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid | 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1h-indol-3-yl}acetic acid |
| 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid | 2-{1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2methylindol-3-yl}acetic acid | 4kyk |
| 5-22-05-00239 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) | 53-86-1 | 74252-25-8 |
| 87377-08-0 | AB00052022 | AB00052022-20 |
| AB00052022-21 | AB00052022_23 | AB00052022_24 |
| AB1009492 | AC-532 | ACT02579 |
| AKOS000592893 | ANW-42683 | ARONIS27005 |
| Aconip | Aconip (TN) | Amuno |
| Arthrexin | Artracin | Artrinovo |
| Artrivia | BCP18951 | BDBM17638 |
| BIDD:GT0132 | BIM-0050670.0001 | BP-30207 |
| BPBio1_000160 | BRD-K57222227-001-06-1 | BRD-K57222227-001-18-6 |
| BRD-K57222227-001-27-7 | BRN 0497341 | BSPBio_000144 |
| BSPBio_001149 | BSPBio_002176 | Bio2_000405 |
| Bio2_000885 | Bonidin | Bonidon |
| Bonidon Gel | C01926 | CAS-53-86-1 |
| CCG-40186 | CCRIS 3502 | CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA- |
| CGIGDMFJXJATDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | CHEBI:49662 | CHEMBL6 |
| CS-2242 | CTK3J2195 | Catlep |
| Certified Reference Material | Chibro-amuno | Chrono-indicid |
| Chrono-indocid | Confortid | D00141 |
| DB-052413 | DB00328 | DSSTox_CID_740 |
| DSSTox_GSID_20740 | DSSTox_RID_75763 | DTXSID9020740 |
| DivK1c_000271 | Dolcidium | Dolcidium PL |
| Dolovin | Durametacin | EC 200-186-5 |
| EINECS 200-186-5 | EU-0100692 | Elmetacin |
| FLAM | FT-0603227 | Flexin continus |
| GTPL1909 | H911 | HMS1362I11 |
| HMS1568H06 | HMS1792I11 | HMS1920F21 |
| HMS1990I11 | HMS2089N19 | HMS2091N09 |
| HMS2095H06 | HMS2231J10 | HMS3262K05 |
| HMS3268A14 | HMS3374F07 | HMS3403I11 |
| HMS3414N13 | HMS3430L03 | HMS3649K17 |
| HMS3655O04 | HMS3678N11 | HMS3712H06 |
| HMS3747K21 | HMS500N13 | HSDB 3101 |
| HY-14397 | Hicin | I 7378 |
| I0655 | IDI1_000271 | IDI1_002160 |
| IMN | Idomethine | Imbrilon |
| InChI=1/C19H16ClNO4/c1-11-15(10-18(22)23)16-9-14(25-2)7-8-17(16)21(11)19(24)12-3-5-13(20)6-4-12/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23) | Inacid | Indacin |
| Indameth | Indmethacine | Indo-Lemmon |
| Indo-Spray | Indo-phlogont | Indo-rectolmin |
| Indo-tablinen | Indochron E-R | Indocid |
| Indocid (pharmaceutical) | Indocin | Indocin (TN) |
| Indocin Sr | Indocin-SR | Indocollyre |
| Indolar SR | Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- | Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- (8CI) |
| Indomecol | Indomed | Indomee |
| Indomet 140 | Indometacin (JP17/INN) | Indometacin 1.0 mg/ml in Acetonitrile |
| Indometacin [INN] | Indometacina | Indometacina [INN-Spanish] |
| Indometacine | Indometacine [INN-French] | Indometacinum |
| Indometacinum [INN-Latin] | Indometacyna | Indometacyna [Polish] |
| Indomethacin & MAP-30 | Indomethacin (Indocid, Indocin) | Indomethacin (USP) |
| Indomethacin [USAN:BAN] | Indomethacin [USAN:USP] | Indomethacin(Indocid) |
| Indomethacin, >=99% (TLC) | Indomethacin, >=99.0% (TLC) | Indomethacin, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only |
| Indomethacin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Indomethacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard | Indomethacin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard |
| Indomethacin, meets USP testing specifications | Indomethacin,(S) | Indomethacine |
| Indomethacinum | Indomethancin | Indomethazine |
| Indomethegan | Indomethine | Indometicina |
| Indometicina [Spanish] | Indomo | Indomod |
| Indonol | Indoptic | Indoptol |
| Indorektal | Indoxen | Inflazon |
| Infrocin | Innamit | Inteban |
| Inteban sp | J10170 | KBio1_000271 |
| KBio2_000489 | KBio2_001399 | KBio2_003057 |
| KBio2_003967 | KBio2_005625 | KBio2_006535 |
| KBio3_000897 | KBio3_000898 | KBio3_001396 |
| KBioGR_000395 | KBioGR_000489 | KBioSS_000489 |
| KBioSS_001399 | KS-00000WRK | KS-000048I8 |
| KS-5255 | KSC492C9L | Kwas 1-(p-chlorobenzoilo)-2-metylo-5-metoksy-3-indolilooctowy |
| Kwas 1-(p-chlorobenzoilo)-2-metylo-5-metoksy-3-indolilooctowy [Polish] | L000959 | LP00692 |
| LS-187 | LS-82147 | Lausit |
| Lopac-I-7378 | Lopac0_000692 | MCULE-5636486088 |
| MFCD00057095 | MLS000069402 | MLS001074194 |
| MLS006011845 | Metacen | Metartril |
| Methazine | Metindol | Mezolin |
| Miametan | Mikametan | Mobilan |
| MolMap_000032 | N-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolylacetic acid | N-p-Chlorbenzoyl-5-methoxy-2-methylindole-3-acetic acid |
| NCGC00015562-01 | NCGC00015562-02 | NCGC00015562-03 |
| NCGC00015562-04 | NCGC00015562-05 | NCGC00015562-06 |
| NCGC00015562-07 | NCGC00015562-08 | NCGC00015562-09 |
| NCGC00015562-10 | NCGC00015562-11 | NCGC00015562-12 |
| NCGC00015562-13 | NCGC00015562-14 | NCGC00015562-15 |
| NCGC00015562-16 | NCGC00015562-17 | NCGC00015562-18 |
| NCGC00015562-19 | NCGC00015562-20 | NCGC00015562-21 |
| NCGC00015562-22 | NCGC00015562-24 | NCGC00015562-25 |
| NCGC00024135-02 | NCGC00024135-04 | NCGC00024135-05 |
| NCGC00024135-06 | NCGC00024135-07 | NCGC00024135-08 |
| NCGC00024135-09 | NCGC00024135-10 | NCGC00024135-11 |
| NCGC00024135-12 | NCGC00024135-13 | NCGC00024135-14 |
| NCGC00024135-15 | NCGC00254075-01 | NCGC00259340-01 |
| NCGC00261377-01 | NCI-C56144 | NCI60_041708 |
| NE11089 | NINDS_000271 | NSC-757061 |
| NSC757061 | Opera_ID_56 | Oprea1_686105 |
| Osmosin | Pharmakon1600-01500350 | Prestwick0_000272 |
| Prestwick1_000272 | Prestwick2_000272 | Prestwick3_000272 |
| Prestwick_597 | PubChem17620 | Q-201239 |
| Q409231 | RTR-019032 | Reumacide |
| Rheumacin LA | S00108 | SBB057417 |
| SBI-0050670.P004 | SC-17536 | SCHEMBL9300 |
| SMR000058195 | SPBio_000979 | SPBio_002363 |
| SPECTRUM1500350 | SR-01000000014 | SR-01000000014-10 |
| SR-01000000014-16 | SR-01000000014-2 | SR-01000000014-4 |
| SR-01000000014-6 | ST24039048 | ST50320042 |
| STL257874 | SW196768-5 | Sadoreum |
| Spectrum2_000970 | Spectrum3_000468 | Spectrum4_000018 |
| Spectrum5_000868 | Spectrum_000919 | TR-019032 |
| Tannex | Tivorbex | Tocris-1708 |
| Tox21_113109 | Tox21_113109_1 | Tox21_201791 |
| Tox21_300266 | Tox21_500692 | UNII-XXE1CET956 |
| UPCMLD-DP023 | UPCMLD-DP023:001 | Vonum |
| XXE1CET956 | Z56784896 | ZINC601283 |
| [1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid | [1-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl]acetic acid # | alpha-(1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-2-methyl-5-methoxy-3-indolyl)acetic acid |
| indometacin | indomethacin | s1723 |
| {1-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl}acetic acid |
| DrugBank Name | Indomethacin |
| DrugBank | DB00328 |
| CAS Number | 28751-45-3, 36798-16-0, 53-86-1, 87377-08-0 |
| PubChem Compound | 3715 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C01926 |
| KEGG Drug | D00141 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46508291 |
| ChEBI | 49662 |
| PharmGKB | PA449982 |
| ChemSpider | 3584 |
| BindingDB | 17638.0 |
| TTD | DAP000617 |
| Wikipedia | Indomethacin |
| HET | IMN |
| DPD | 10126 |