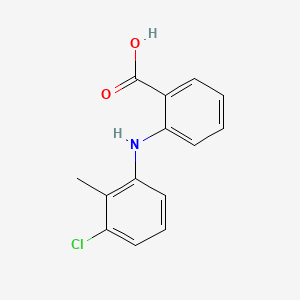
Drug
D0122 | Tolfenamic Acid
M
M01AG02 Tolfenamic acid
[M01AG] Fenamates
[M01A] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS, NON-STEROIDS
[M01] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS
[M] Musculoskeletal system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 122 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE) | decrease | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| PROTONOPHORIC UNCOUPLING | 278 | |||||||
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 11.88±0.00 | human | qHTS-HepG2 | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 17.34 | human | HepG2 | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 14.81±4.38 | rat | hepatocytes | MMP assay | decrease | IC50 | 163 | |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 263.8 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 238.7 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| STATE 2 RESPIRATION | 3.4 ± 0.6 | rat | isolated rat liver mitochondria | State 2 respiration ( 96-well plate format using a phosphorescent oxygen-sensitive probe MitoXpress) | inhibit | UC50 (nmol/mg mitochondrial protein) | 40 | |
| STATE 3 RESPIRATION | 100 nmol/mg mitochondrial protein | rat | isolated rat liver mitochondria | State 3 respiration ( 96-well plate format using a phosphorescent oxygen-sensitive probe MitoXpress) | Negative | IC50 (nmol/mg mitochondrial protein) | 40 | |
| LIPID METABOLISM | 83.1 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | LipidTox, for neutral lipid accumulation, to evaluate lipid content. | accumulation | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| GLUTATHIONE METABOLISM | 105 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | glutathion depletion: cells were incubated with 50 μM monochlorobimane with 6 μg/ml Hoechst 33342 | AC50 (μM) | 40 | |
| SWELLING | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| ROS PRODUCTION | NR | rat | hepatocytes | use CM-H2DCFDA to monitor reactive oxygen species | Negative | AC50 (μM) | 40 | |
| CYTOCHROME C RELEASE | 75 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | cytochrome c release (anti-cytochrome c antibody ) | induce | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| ER STRESS-INDUCED | 50 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | DNA damage 153 induction (GADD153 antibodies) for ER-stress induced apoptosis | induce | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | > 400 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Cytochrome c | > 400 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 197 companies from 2 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. H301 (98.48%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P264, P270, P301+P310, P321, P330, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| 13710-19-5 | 2(3-Chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic acid | 2-((3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)benzoic acid |
| 2-(3-Chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic acid | 2-(3-Chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic acid # | 2-(3-Chloro-o-toluidino)benzoic Acid |
| 2-(3-chloro-2-methylphenylamino)benzoic acid | 2-([3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl]amino)benzoic acid | 2-[(3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]benzoic Acid |
| 2-[(3-chloranyl-2-methyl-phenyl)amino]benzoic acid | 3G943U18KM | A807198 |
| AB00052244 | AB00052244-15 | AB00052244_16 |
| AB00052244_17 | AB0032595 | AB2000392 |
| ACMC-209cat | AK305709 | AKOS012836098 |
| ANW-20211 | API0002084 | AS-13748 |
| Acide tolfenamique | Acido tolfenamico | Acidum tolfenamicum |
| Anthranilic acid, N-(3-chloro-o-tolyl)- | BDBM35905 | BIDD:GT0343 |
| BPBio1_000209 | BRD-K50133271-001-05-4 | BRD-K50133271-001-10-4 |
| BSPBio_000189 | BSPBio_003223 | Benzoic acid, 2-((3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino)- (9CI) |
| Benzoic acid, 2-(3-chloro-2-methylphenylamino)- | Benzoic acid, 2-[(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]- | Bifenac |
| CAS-13710-19-5 | CCG-39189 | CHEBI:32243 |
| CHEMBL121626 | CS-2377 | Certified Reference Material |
| Clotam | Clotam (TN) | D01183 |
| DA-11289 | DB09216 | DSSTox_CID_25409 |
| DSSTox_GSID_45409 | DSSTox_RID_80860 | DTXSID1045409 |
| FT-0652603 | GEA 6414 | GTPL8769 |
| HMS1568J11 | HMS1921P13 | HMS2090D04 |
| HMS2095J11 | HMS2230J13 | HMS3370A02 |
| HMS3651E06 | HMS3712J11 | HY-B0335 |
| InChI=1/C14H12ClNO2/c1-9-11(15)6-4-8-12(9)16-13-7-3-2-5-10(13)14(17)18/h2-8,16H,1H3,(H,17,18) | J-006962 | J10240 |
| KBio2_001743 | KBio2_004311 | KBio2_006879 |
| KBio3_002723 | KBioGR_000935 | KBioSS_001743 |
| KS-00000H6I | MCULE-9901889833 | MLS000028531 |
| N-(2-Methyl-3-chlorophenyl)anthranilic acid | N-(3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl)anthranilic acid | N-(3-Chloro-o-tolyl)-anthranilic acid |
| NCGC00016705-01 | NCGC00016705-02 | NCGC00016705-03 |
| NCGC00016705-04 | NCGC00016705-05 | NCGC00016705-06 |
| NCGC00016705-07 | NCGC00016705-10 | NCGC00022587-03 |
| NCGC00022587-04 | NCGC00022587-05 | NSC-757873 |
| NSC757873 | Oprea1_692996 | Pharmakon1600-01501198 |
| Prestwick0_000205 | Prestwick1_000205 | Prestwick2_000205 |
| Prestwick3_000205 | Prestwick_579 | Q59412 |
| SBB058187 | SBI-0051687.P002 | SCHEMBL25190 |
| SEL10850963 | SMR000058289 | SPBio_001311 |
| SPBio_002110 | SPECTRUM1501198 | SR-01000000102 |
| SR-01000000102-2 | SR-01000000102-3 | ST51015128 |
| SW196753-3 | Spectrum2_001446 | Spectrum3_001762 |
| Spectrum4_000238 | Spectrum5_001143 | Spectrum_001263 |
| TC-108956 | Tolfedine | Tolfenamic |
| Tolfenamic Acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard | Tolfenamic acid (JAN/INN) | Tolfenamic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard |
| Tolfenamic acid, NSAID | Tolfenamic acid, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard | Tolfine |
| Tox21_110570 | Tox21_110570_1 | UNII-3G943U18KM |
| UNM000001237003 | X5948 | YEZNLOUZAIOMLT-UHFFFAOYSA- |
| YEZNLOUZAIOMLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ZINC2188 | cid_610479 |
| flufenamic acid analogue, 32 | n-(3-chloro-ortho-tolyl)anthranilic acid | s1959 |
| tolfenamic acid | tolfenamic-acid |
| DrugBank Name | Tolfenamic Acid |
| DrugBank | DB09216 |
| CAS Number | 13710-19-5 |
| PubChem Compound | 610479 |
| KEGG Drug | D01183 |
| PubChem.Substance | 310265123 |
| ChEBI | 32243 |
| PharmGKB | PA166049189 |
| ChemSpider | 530683 |
| BindingDB | 35905.0 |
| Wikipedia | Tolfenamic_acid |
| HET | TLF |
| DPD | 928 |
1. Chan et al. (2005)