D0422 | Clotrimazole
D
G
A
G01AF20 Combinations of imidazole derivatives
[G01AF] Imidazole derivatives
[G01A] ANTIINFECTIVES AND ANTISEPTICS, EXCL. COMBINATIONS WITH CORTICOSTEROIDS
[G01] GYNECOLOGICAL ANTIINFECTIVES AND ANTISEPTICS
[G] Genitourinary system and reproductive hormones
G01AF02 Clotrimazole
[G01AF] Imidazole derivatives
[G01A] ANTIINFECTIVES AND ANTISEPTICS, EXCL. COMBINATIONS WITH CORTICOSTEROIDS
[G01] GYNECOLOGICAL ANTIINFECTIVES AND ANTISEPTICS
[G] Genitourinary system and reproductive hormones
D01AC01 Clotrimazole
[D01AC] Imidazole and triazole derivatives
[D01A] ANTIFUNGALS FOR TOPICAL USE
[D01] ANTIFUNGALS FOR DERMATOLOGICAL USE
[D] Dermatological drugs
A01AB18 Clotrimazole
[A01AB] Antiinfectives and antiseptics for local oral treatment
[A01A] STOMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[A01] STOMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 23.9 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 2.9 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| GLYCOLYSIS | decrease | 35 | ||||||
| SWELLING | ND | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 2.1875-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | increase | 1.35-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 3.1818-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | increase | 1.5-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 3.3333-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | increase | 1.5882-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 1.3953-fold increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | Negative | No increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 1.3953-fold increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | increase | 1.2623-fold increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | increase | 2.3256-fold increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | increase | 1.6223-fold increase | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 150 mg/kg/day | 6 days a week for two weeks | human | CAL27(xenograft tumors)/mouse | Immunohistochemistry | increase | 1.5-fold decrease | 5 |
| APOPTOSIS | 150 mg/kg/day | 6 days a week for two weeks | human | CAL27(xenograft tumors)/mouse | western blot analysis | increase | 2.0-fold increase | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | SCC25 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | UM1 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | SCC25 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| EARLY APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | UM1 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | SCC25 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 30 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | UM1 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.05 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | SCC25 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| LATE APOPTOSIS | 40 μmol/L | 24 hours | human | UM1 | Apoptosis measurement | increase | p < 0.01 | 5 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 2.9 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | inhibitor | 2.1875-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | inhibitor | 1.35-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | inhibitor | 3.1818-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | inhibitor | 1.5-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | inhibitor | 3.3333-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | inhibitor | 1.5882-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 | 150 mg/kg/day | 6 days a week for two weeks | human | CAL27(xenograft tumors)/mouse | Immunohistochemistry | inhibitor | 1.5-fold decrease | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | activate | 1.3953-fold increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 12 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | Negative | No increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | activate | 1.3953-fold increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 24 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | activate | 1.2623-fold increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | CAL27 | western blot | activate | 2.3256-fold increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 40 µM | 48 hours | human | UM1 | western blot | activate | 1.6223-fold increase | 5 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX | 150 mg/kg/day | 6 days a week for two weeks | human | CAL27(xenograft tumors)/mouse | western blot analysis | activate | 2.0-fold increase | 5 |
| Cytochrome c | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
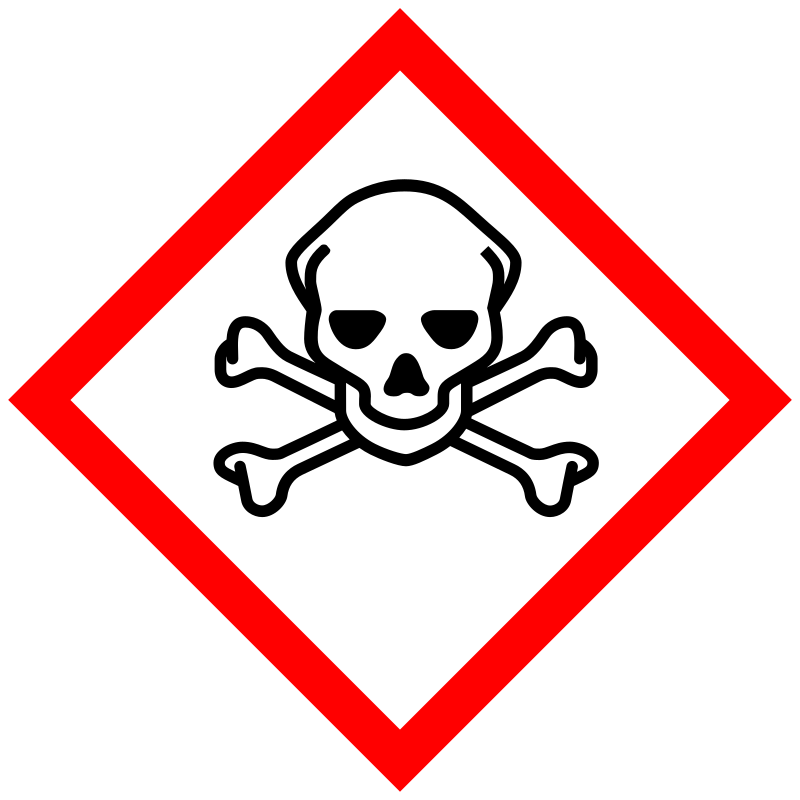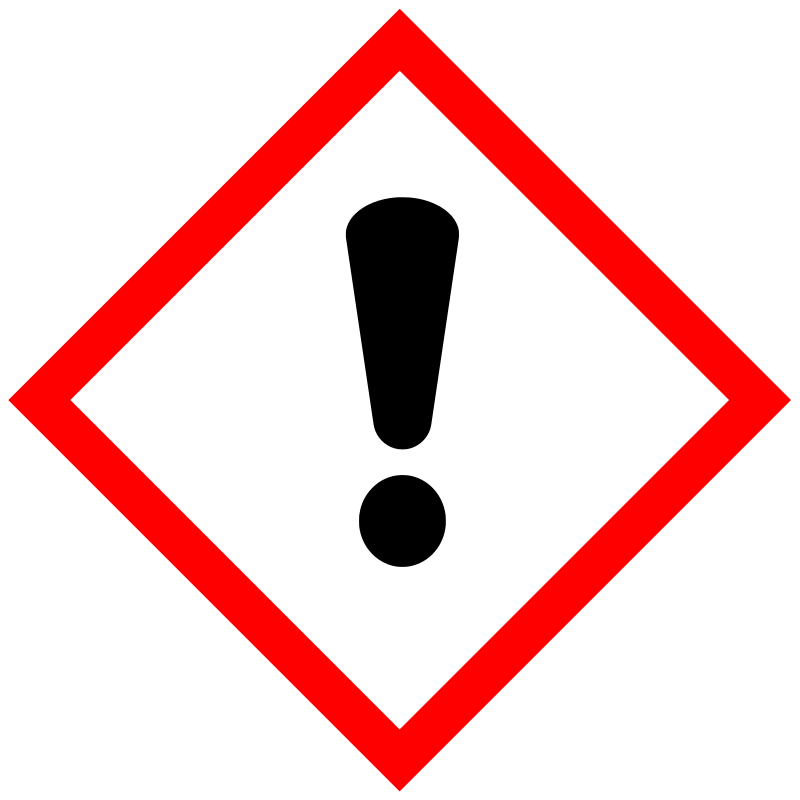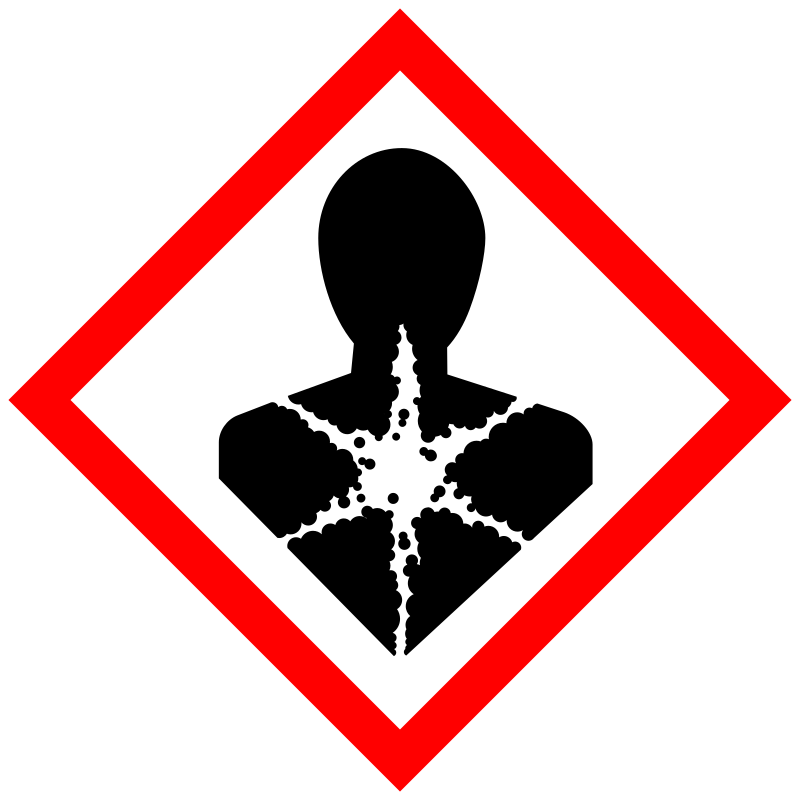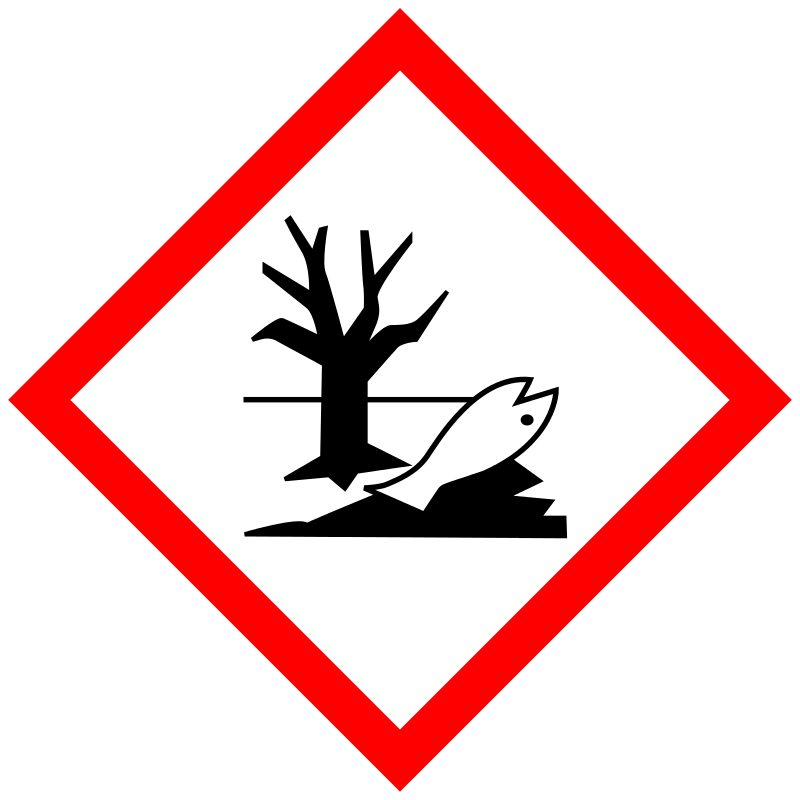    |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 331 companies from 14 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 3 of 331 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 12 notification(s) provided by 328 of 331 companies with hazard statement code(s): H302 (99.09%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H311 (10.67%): Toxic in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal] H315 (80.18%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (90.85%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H361 (10.67%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H373 (10.67%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H400 (83.84%): Very toxic to aquatic life [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard] H410 (84.45%): Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Warning Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P361, P362, P363, P391, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mammal (species unspecified) | LD50 | oral | 750mg/kg (750mg/kg) | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy Vol. -, Pg. 271, 1969. | |
| women | TDLo | intravaginal | 28mg/kg/7D (28mg/kg) | skin and appendages (skin): primary irritation: after topical exposure | Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 18, Pg. 41, 1981. |
| rat | LDLo | subcutaneous | 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 7, Pg. 1333, 1973. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intravenous | 198mg/kg (198mg/kg) | Gekkan Yakuji. Pharmaceuticals Monthly. Vol. 9, Pg. 759, 1967. | |
| cat | LD50 | oral | > 1gm/kg (1000mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 22, Pg. 1272, 1972. |
| rabbit | LD50 | oral | > 1gm/kg (1000mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 22, Pg. 1272, 1972. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 708mg/kg (708mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 22, Pg. 1272, 1972. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 761mg/kg (761mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 22, Pg. 1272, 1972. | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 108mg/kg (108mg/kg) | Drug and Chemical Toxicology. Vol. 13, Pg. 195, 1990. | |
| dog | LD50 | oral | > 2gm/kg (2000mg/kg) | gastrointestinal: nausea or vomiting | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 22, Pg. 1272, 1972. |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 445mg/kg (445mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 7, Pg. 1333, 1973. | |
| mouse | LDLo | subcutaneous | 10gm/kg (10000mg/kg) | Kiso to Rinsho. Clinical Report. Vol. 7, Pg. 1333, 1973. | |
| (2-Chlorophenyl)diphenyl-1-imidazolylmethane | (Chlorotrityl)imidazole | 1-((2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl)-1H-imidazole |
| 1-((2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl)-1H-imidazole (9CI) | 1-((o-Chloro-phenyl)diphenylmethyl)imidazole | 1-(.alpha.-(2-Chlorophenyl)benzhydryl)imidazole |
| 1-(2-Chloro-?,?-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole | 1-(2-chlorotrityl)imidazole | 1-(alpha-(2-Chlorophenyl)benzhydryl)imidazole |
| 1-(o-Chloro-.alpha.,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole | 1-(o-Chloro-alpha,alpha-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole | 1-(o-Chloro-|A,|A-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole |
| 1-(o-Chlorophenyldiphenylmethyl)imidazole | 1-(o-Chlorotrityl)imidazole | 1-(o-Chlorotrityl)imidazole |
| 1-(o-chloro-a,a-diphenylbenzyl)imidazole | 1-[(2-Chloro-phenyl)-diphenyl-methyl]-1H-imidazole | 1-[(2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-1H-imidazole |
| 1-[(2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-1H-imidazole | 1-[(2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]imidazole | 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)(diphenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole |
| 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-di(phenyl)methyl]imidazole | 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenyl-methyl]imidazole | 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenylmethyl]imidazole |
| 1H-Imidazole, 1-((2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl)- | 1H-Imidazole, 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)-diphenylmethyl] | 1H-Imidazole, 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]- |
| 23593-75-1 | 3ACDFDF8-38E3-4368-85D0-BDF8AE1E6591 | 455-EP2272972A1 |
| 455-EP2272973A1 | 455-EP2275420A1 | 455-EP2277872A1 |
| 455-EP2281816A1 | 455-EP2292595A1 | 455-EP2295055A2 |
| 455-EP2295416A2 | 455-EP2298748A2 | 455-EP2298764A1 |
| 455-EP2298765A1 | 455-EP2305642A2 | 455-EP2311453A1 |
| 455-EP2311808A1 | 455-EP2311829A1 | 5-23-04-00291 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) |
| 593C751 | A816789 | AB00051951 |
| AB00051951-14 | AB00051951_15 | AB00051951_16 |
| AB0015989 | AB1009401 | AKOS005607024 |
| API0002086 | AS-13816 | B 5097 |
| BAY 5097 | BAY b 5097 | BAY b5097 |
| BAY-5097 | BAYb 5097 | BCP02150 |
| BDBM31774 | BIDD:GT0450 | BIDD:PXR0036 |
| BPBio1_000126 | BRD-K15916496-001-14-7 | BRN 0622318 |
| BSPBio_000114 | BSPBio_002057 | Bay b 9057 |
| Bay-B 5097 | Bis-fenil-(2-clorofenil)-1-imidazolil-metano | Bis-fenil-(2-clorofenil)-1-imidazolil-metano [Italian] |
| Bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)(1-imidazoyl)methane | Bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazoyl)methane | Bisphenyl-(2-chlorphenyl)-1-imidazolyl-methan |
| Bisphenyl-(2-chlorphenyl)-1-imidazolyl-methan [German] | C 6019 | C06922 |
| CAS-23593-75-1 | CCG-35563 | CCRIS 6245 |
| CHEBI:3764 | CHEMBL104 | CLT |
| CPD000058306 | CS-1926 | Canesten |
| Canesten 1-Day Cream Combi-Pak | Canesten 1-Day Therapy | Canesten 3-Day Therapy |
| Canesten 6-Day Therapy | Canesten Combi-Pak 1-Day Therapy | Canesten Combi-Pak 3-Day Therapy |
| Canesten Cream | Canesten Solution | Canestene |
| Canestine | Canifug | Certified Reference Material |
| Chlotrimazole | Clomatin | Clotrimaderm |
| Clotrimaderm Cream | Clotrimazol | Clotrimazol [INN-Spanish] |
| Clotrimazole (Canesten) | Clotrimazole (JP17/USP/INN) | Clotrimazole [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN] |
| Clotrimazole [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | Clotrimazole for peak identification, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Clotrimazole(Canesten) |
| Clotrimazole, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard | Clotrimazole, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Clotrimazole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard |
| Clotrimazole, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard | Clotrimazole, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard | Clotrimazole,(S) |
| Clotrimazolum | Clotrimazolum [INN-Latin] | Cutistad |
| D00282 | DB-046195 | DB00257 |
| DRG-0072 | DSSTox_CID_9871 | DSSTox_GSID_29871 |
| DSSTox_RID_78827 | DTXSID7029871 | Desamix F |
| Diphenyl(2-chlorophenyl)(1-imidazolyl)methane | Diphenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazolylmethane | DivK1c_000665 |
| EINECS 245-764-8 | EU-0100315 | Empecid |
| Esparol | FB 5097 | FB b 5097 |
| FT-0603193 | Fem Care | FemCare |
| G07GZ97H65 | GNF-Pf-3499 | GTPL2330 |
| Gino-Lotremine | Gyne lotrimin | Gyne-Lotrimin |
| Gyne-Lotrimin 3 | Gyne-Lotrimin 3 Combination Pack | Gyne-Lotrimin Combination Pack |
| Gyne-Lotrimin3 | Gyne-Lotrimin3 Combination Pack | Gynix |
| HMS1568F16 | HMS1920O21 | HMS2051E11 |
| HMS2091G10 | HMS2095F16 | HMS2235E20 |
| HMS3260P12 | HMS3369I03 | HMS3393E11 |
| HMS3655I09 | HMS3712F16 | HMS502B07 |
| HSDB 3266 | HY-10882 | IDI1_000665 |
| Imidazole, 1-(o-chloro-.alpha.,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)- | Imidazole, 1-(o-chloro-alpha,alpha-diphenylbenzyl)- | Imidazole,.alpha.-diphenylbenzyl)- |
| J10369 | Jidesheng | KBio1_000665 |
| KBio2_001823 | KBio2_004391 | KBio2_006959 |
| KBio3_001277 | KBioGR_000850 | KBioSS_001823 |
| KS-00000XNX | Kanesten | Klotrimazole |
| LP00315 | LS-78271 | Lopac-C-6019 |
| Lopac0_000315 | Lotrimax | Lotrimin |
| Lotrimin (TN) | Lotrimin AF Cream | Lotrimin AF Jock-Itch Cream |
| Lotrimin AF Lotion | Lotrimin AF Solution | Lotrimin Af |
| Lotrimin Cream | Lotrimin Lotion | Lotrimin Solution |
| MCULE-6862012558 | MFCD00057220 | MLS000028502 |
| MLS000758243 | MLS001423972 | MRF-0000070 |
| Methane, bis-phenyl-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-imidazolyl- | Mono-baycuten | Monobaycuten |
| Mycelax | Mycelex | Mycelex (TN) |
| Mycelex 7 | Mycelex Cream | Mycelex G |
| Mycelex OTC | Mycelex Solution | Mycelex Troches |
| Mycelex Twin Pack | Mycelex-7 | Mycelex-7 Combination Pack |
| Mycelex-G | Mycelex: MycosporinRimazole | Myclo Cream |
| Myclo Solution | Myclo Spray Solution | Myclo-Gyne |
| Mycofug | Mycosporin | Mykosporin |
| N713 | NC00035 | NCGC00015251-01 |
| NCGC00015251-02 | NCGC00015251-03 | NCGC00015251-04 |
| NCGC00015251-05 | NCGC00015251-06 | NCGC00015251-07 |
| NCGC00015251-08 | NCGC00015251-09 | NCGC00015251-10 |
| NCGC00015251-11 | NCGC00015251-13 | NCGC00015251-14 |
| NCGC00093761-01 | NCGC00093761-02 | NCGC00093761-03 |
| NCGC00093761-04 | NCGC00093761-05 | NCGC00093761-06 |
| NCGC00254538-01 | NCGC00261000-01 | NCIMech_000609 |
| NINDS_000665 | NSC 257473 | NSC-257473 |
| NSC-756700 | NSC257473 | NSC756700 |
| Nalbix | Neo-Zol Cream | Otomax |
| Pan-Fungex | Pedisafe | Pharmakon1600-01500200 |
| Prestwick0_000267 | Prestwick1_000267 | Prestwick2_000267 |
| Prestwick3_000267 | Prestwick_120 | Q413546 |
| QTL1_000024 | Rimazole | SAM001247056 |
| SB17418 | SBI-0050303.P004 | SC-17936 |
| SCHEMBL3850 | SMR000058306 | SPBio_000176 |
| SPBio_002333 | SPECTRUM1500200 | SR-01000075771 |
| SR-01000075771-1 | SR-01000075771-10 | SR-01000075771-6 |
| SR-01000075771-8 | ST50994242 | STK700023 |
| SW196431-5 | Spectrum2_000128 | Spectrum3_000359 |
| Spectrum4_000295 | Spectrum5_000781 | Spectrum_001343 |
| Stiemazol | Tibatin | Tox21_110111 |
| Tox21_110111_1 | Tox21_300415 | Tox21_500315 |
| Trimysten | Trivagizole 3 | UNII-G07GZ97H65 |
| VNFPBHJOKIVQEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | Veltrim | W-107394 |
| ZINC3807804 | [(2-chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]imidazole | chlortrimazole |
| cid_2812 | clortrimazole | clotrimazole |
| clotrimazole crystalline | clotrimeizol | component of Lotrimax (Salt/Mix) |
| component of Otomax (Salt/Mix) | s1606 |
| DrugBank Name | Clotrimazole |
| DrugBank | DB00257 |
| CAS Number | 117829-71-7, 1185076-41-8, 23593-75-1 |
| PubChem Compound | 2812 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C06922 |
| KEGG Drug | D00282 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46507927 |
| ChEBI | 3764 |
| PharmGKB | PA449057 |
| ChemSpider | 2710 |
| BindingDB | 31774.0 |
| TTD | DAP000138 |
| Wikipedia | Clotrimazole |