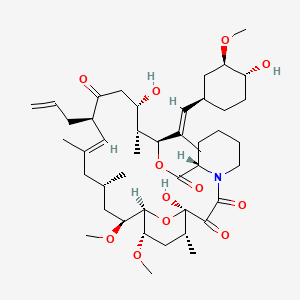
D0505 | tacrolimus
D
L
L04AD02 Tacrolimus
[L04AD] Calcineurin inhibitors
[L04A] IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS
[L04] IMMUNOSUPPRESSANTS
[L] Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
D11AH01 Tacrolimus
[D11AH] Agents for dermatitis, excluding corticosteroids
[D11A] OTHER DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[D11] OTHER DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[D] Dermatological drugs
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNCOUPLING | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | measurements of mitochondrial respiration; RST inhibition assay, RST uncoupling assay; IC 50ratio of glucose/galactose assay | Negative | 53 | |||
| RESPIRATORY CONTROL RATIO (RCR) | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was measured with a Clark‐type electrode | decrease | 10% | 323 | |
| RESPIRATORY CONTROL RATIO (RCR) | 3.4E−11 M and 2.3E−8 M | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was measured with a Clark‐type electrode | decrease | EC50 ; maximal inhibitory effect was about 20% | 323 | |
| BASAL RESPIRATION | 50 µg/ml | 12hr | INS-1 cells | XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer | decrease | 322 | ||
| MAXIMAL RESPIRATION | 50 µg/ml | 12hr | INS-1 cells | XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer | decrease | 322 | ||
| PROTON LEAK | 50 µg/ml | 12hr | INS-1 cells | XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer | decrease | 322 | ||
| NON-MITOCHONDRIAL RESPIRATION | 50 µg/ml | 12hr | INS-1 cells | XF24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer | decrease | 322 | ||
| P/O RATIO ( ADP/O) | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was measured with a Clark‐type electrode | decrease | 323 | ||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | decrease | 68 | ||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | rat | isolated liver mitochondria | measurements of mitochondrial respiration; RST inhibition assay, RST uncoupling assay; IC 50ratio of glucose/galactose assay | Negative | 53 | |||
| TRANSPORT OF CALCIUM | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Ca2+ fluxes: A specific Ca2+ electrode (Orion 9320) fitted to a Hansatech recorder via a 720A Orion ionometer was used to record Ca2+ movements in extramitochondrial medium in a thermostat‐controlled reaction chamber. | Negative | 323 | ||
| SWELLING | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Measurement of swelling of energized mitochondria: measuring the decrease of optical density at 520 nm, with a Hitachi spectrophotometer (U3000) | Negative | 323 | ||
| VOLUME | beta cells from isolated rat islets | Transmission electron microscopy and 3D reconstruction of mitochondria | decrease | 322 | ||||
| ROS PRODUCTION | 50 µg/ml | 12hr | INS-1 cells | MitoSOX Red staining to detect mitochondrial superoxide anion (O2−) levels by flow cytometric analysis and e time-lapse images of cells treated for 12 h with MitoSOX Red. | induce | 322 | ||
| CYTOCHROME C RELEASE | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | The amount of cytochrome c was measured using a Quantikine® M Rat/Mouse Cytochrome c immunoassay after addition of drugs in energized mitochondrial (3 min) or after Ca2+‐induced mitochondrial swelling (3 min). | Negative | 323 | ||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | 1 μM | rat | isolated kidney mitochondria | Mitochondrial complex III assay (ubiquinol‐cytochrome c oxidoreductase) | inhibit | 30% | 323 | |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
  |
Danger |
The GHS information provided by 1 company from 1 notification to the ECHA C&L Inventory. H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H361 (100%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H372 (100%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] |
P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P281, P301+P310, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
  |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 203 companies from 8 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H301 (99.01%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H361 (97.54%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H372 (97.04%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P281, P301+P310, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
 |
Danger |
H301: Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] |
P264, P270, P301+P310, P321, P330, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| (-)-FK 506 | (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,19-dihydroxy-3-{(1E)-1-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]prop-1-en-2-yl}-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(prop-2-en-1-yl)-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-3H-15,19-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone | (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,19-dihydroxy-3-{(E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethenyl}-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-prop-2-en-1-yl-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-3H-15,19-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone |
| (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-Hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[(1E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propen-1-yl)-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)tetrone | (E)-(1R,9S,12S,13R,14R,21S,23S,24R,25S,27R)-17-Allyl-1,14-dihydroxy-12-[(E)-2-((3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-cyclohexyl)-1-methyl-vinyl]-23,25-dimethoxy-13,19,21,27-tetramethyl-11,28-dioxa-4-aza-tricyclo[22.3.1.0*4,9*]octacos-18-ene-2,3,10,16-tetraone | 104987-11-3 |
| 15,19-Epoxy-3H-pyrido(2,1-c)(1,4)oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-(2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl)-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propenyl)-, (3S-(3R*(E(1S*,3S*,4S*)),4S*,5R*,8S*,9E,12R*,14R*,15S*,16R*,18S*,19S*,26aR*))- | 15,19-Epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)-tetrone, 5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[(1E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyc | 15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(23H)-tetrone, |
| 4,5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-heptadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3- | 581T933 | 8-DEETHYL-8-[BUT-3-ENYL]-ASCOMYCIN |
| AB0012538 | AB01209746-01 | AB01209746_03 |
| ABP000474 | AC-1182 | AKOS005145901 |
| AM81227 | AT-2441 | Advagraf |
| Anhydrous Tacrolimus | Astagraf XL | Avagraf |
| BDBM50030448 | BDBM50079777 | BRD-K35452788-001-02-1 |
| BRD-K69608737-001-03-7 | BRD-K69608737-001-10-2 | BSPBio_001279 |
| C01375 | C44H69NO12 | CAS-104987-11-3 |
| CCRIS 7124 | CHEBI:61049 | CHEBI:93221 |
| CHEMBL269732 | CHEMBL66247 | CS-1507 |
| D08556 | DB00864 | DSSTox_CID_26354 |
| DSSTox_GSID_46354 | DSSTox_RID_81557 | DTXSID5046354 |
| EN300-221601 | EX-A1677 | Envarsus |
| Envarsus XR | FK 506 | FK-506 (Tacrolimus) |
| FK-506/Tacrolimus | FK506 | FR-900506 |
| FR900506 | FT-0082660 | Fk-506 |
| Fujimycin | Fujimycin|||FK-506|||FR-900506 | GTPL6784 |
| Graceptor | HMS1792O21 | HMS1990O21 |
| HMS2093M19 | HMS3403O21 | HMS503O21 |
| HSDB 8195 | HY-13756 | Hecoria |
| IDI1_001040 | K506 | L 679934 |
| L-679934 | LCP-Tacro | LMPK04000003 |
| M2258 | MFCD11045918 | Modigraf |
| NCGC00163470-01 | NCGC00163470-02 | NCGC00163470-03 |
| NCGC00163470-04 | NCGC00163470-05 | NCGC00163470-06 |
| NCGC00163470-07 | NSC-758659 | NSC758659 |
| Pharmakon1600-01503968 | Prograf | Prograf (TN) |
| Prograft | Protopic | Protopy |
| PubChem18875 | Q-201775 | Q411648 |
| QJJXYPPXXYFBGM-LFZNUXCKSA-N | SBI-0052894.P002 | SC-13591 |
| SCHEMBL3088 | SR-05000001879 | SR-05000001879-1 |
| SR-05000001879-2 | SR-05000001879-5 | TACROLIMUS MONOHYDRATE |
| Tacrolimus (INN) | Tacrolimus (anhydrous) | Tacrolimus [USAN:INN] |
| Tacrolimus [USAN] | Tacrolimus anhydrous | Tacrolimus solution, 1.0 mg/mL in acetonitrile, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material; |
| Tacrolimus, anhydrous | Talymus | Tox21_112056 |
| Tsukubaenolide | UNII-Y5L2157C4J | W-1246 |
| Y5L2157C4J | ZINC169289411 | [(E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethenyl]-14,16- |
| dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propenyl)-,(3S,4R,5S,8R,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)- | lohexyl]-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propen-1-yl)-, (3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)- | s5003 |
| tacrolimus | tacrolimus (fk506) |