Drug
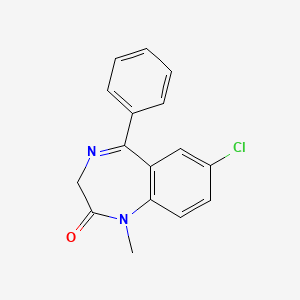
D1422 | Diazepam
N
N05BA01 Diazepam
[N05BA] Benzodiazepine derivatives
[N05B] ANXIOLYTICS
[N05] PSYCHOLEPTICS
[N] Nervous system
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RESPIRATORY STATES | 70 μg/ml | pig kidney embryo cells | polarographic cell (1.2 ml) | inhibit | 293 | |||
| ATP LEVEL | 150μg/ml | 2hr | PE cells | luciferin-luciferase method | decrease | 293 | ||
| FRAGMENTATION | 140μg/ml | 16hr | PE cells | Energy-dependent accumulation of ethylrhodamine ; Electron micrographs of ultrathin sections | induce | 293 | ||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATP synthase | 140μg/ml | PE cells | potentiometric method | inhibit | inhibit 60% | 293 | ||