D0098 | Pioglitazone
A
A10BG03 Pioglitazone
[A10BG] Thiazolidinediones
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10BD12 Pioglitazone and sitagliptin
[A10BD] Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10BD09 Pioglitazone and alogliptin
[A10BD] Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10BD06 Glimepiride and pioglitazone
[A10BD] Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10BD05 Metformin and pioglitazone
[A10BD] Combinations of oral blood glucose lowering drugs
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 10–25 μM | 3min | male CD-1 mice | isolated liver mitochondria | The electrical transmembrane potential of mitochondria was monitored spectrophotometrically with the cationic dye, rhodamine 123, and monitored at the 505/535 nm. | Negative | 331 | |
| TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 50 μM | 3min | male CD-1 mice | isolated liver mitochondria | The electrical transmembrane potential of mitochondria was monitored spectrophotometrically with the cationic dye, rhodamine 123, and monitored at the 505/535 nm. | decrease | p < 0.05, significantly different from the control | 331 |
| TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 25-50 µM | ZDF fa/fa rat & ZDF lean rat | isolated liver mitochondria | The transmembrane potential of the mitochondria was monitored spectrophotometrically using rhodamine-123. | decrease | significantly different from control group (p < 0.05) | 225 | |
| OPENING OF PERMEABILITY TRANSITION PORE (PTP) | 50 μM | male CD-1 mice | isolated liver mitochondria | Mitochondrial swelling as the indicator of mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) was estimated from the decrease in absorbance at 540 nm. | Negative | 331 | ||
| STATE 3 RESPIRATION | decrease | 22 | ||||||
| RESPIRATORY CONTROL RATIO (RCR) | 25-50 μM | ZDF fa/fa rat & ZDF lean rat | isolated liver mitochondria | OCR and measured using a fluorescent oxygen probe (Presens) | decrease | significantly different from control (p < 0.05) | 225 | |
| RESPIRATORY CONTROL RATIO (RCR) | 10-50 μM | ZDF fa/fa rat & ZDF lean rat | isolated liver mitochondria | OCR and measured using a fluorescent oxygen probe (Presens) | Negative | 225 | ||
| OXYGEN CONSUMPTION RATE (OCR) | 100 μM | 2 minutes | human | HepG2 | Measurement of OCR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| OXYGEN CONSUMPTION RATE (OCR) | 100 μM | 2 minutes | feline | cardiomyocytes | Measurement of OCR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | decrease | 22 | ||||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | decrease | 35 | ||||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | decrease | 35 | ||||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | inhibit | 197 | ||||||
| GLYCOLYSIS | 21 | |||||||
| ECAR | 100 μM | 2 minutes | human | HepG2 | Measurement of ECAR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| ECAR | 100 μM | 2 minutes | feline | cardiomyocytes | Measurement of ECAR | Negative | EC50 | 7 |
| GLUCOSE GALACTOSE IC50 RATIO | 300.0 ± 0 ,300.0 ± 0, 1, 300.0 ± 0, 300.0 ± 0, 1 | 4hr | H9c2 cells | high-glucose–galactose cell viability assay with JC-1 mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP-depletion assays (CellTiter-Glo reagent ). | Negative | glucose/galactose IC50 ratio (JC-1 IC50 in glucose, JC-1 IC50 in galactose, JC-1 glu/gla, ATP IC50 in glucose, ATP IC50 in galactose, ATP glu/gla ) | 50 | |
| ACCUMULATION OF CALCIUM | 50 μM | male CD-1 mice | isolated liver mitochondria | Assessment of mitochondrial Ca2+ efflux with arsenazo III at 675/685 nm. | Negative | 331 | ||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | inhibitor | 22 | ||||||
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | inhibitor | 35 | ||||||
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | inhibitor | 35 | ||||||
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Warning |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 5 companies from 3 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. H302+H312+H332 (20%): Harmful if swallowed, in contact with skin or if inhaled [Warning Acute toxicity, oral acute toxicity, dermal acute toxicity, inhalation] H302 (100%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H312 (80%): Harmful in contact with skin [Warning Acute toxicity, dermal] H315 (20%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (20%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H332 (80%): Harmful if inhaled [Warning Acute toxicity, inhalation] H335 (20%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
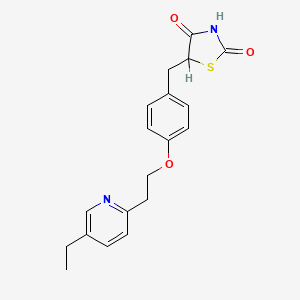
| (+/-)-5-[[4-[2-(5-Ethyl-2-pyridinyl)-ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione | (+/-)-5-[p-[2-(ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione | 105355-27-9 |
| 105390-47-4 | 111025-46-8 | 2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, (+-)- |
| 2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]- (9CI) | 2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-, (+/-)- | 2,4-thiazolidinedione, 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]- |
| 355P279 | 5-(4-(2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy)benzyl)-2,4-thiazolidinedione | 5-(4-(2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)-thiazolidine-2,4-dione |
| 5-(4-(2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy)benzyl)thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-({4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]phenyl}methyl)-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-[4-[2-(5-ETHYL-2-PYRIDYL)ETHOXY]BENZYL]-2,4-THIAZOLIDINEDIONE |
| 5-[4-[2-(5-Ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl]thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl) ethoxy]benzyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione | 5-[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)eth-oxy]benzyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione |
| 5-[[4-[2-(5-Ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl-2,4-thiazolidinedione | 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy] phenyl]methyl]-2,4-thiazolidinedione |
| 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-[[4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]thiazolidine-2,4-dione | 5-[[4-[2-[(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)]ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]thiazolidine- 2,4-dione |
| 5-{4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl}-2,4-thiazolidinedione | 5-{4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridyl)ethoxy]benzyl}-2,4thiazolidinedione | 5-{4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]benzyl}-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione |
| 5-{4-[2-(5-ethylpyridin-2-yl)ethoxy]benzyl}-4-hydroxy-1,3-thiazol-2(5H)-one | A801204 | AB0004710 |
| AB00698454-10 | AB00698454_11 | AB00698454_12 |
| AB00698454_13 | AB1004597 | AB2000683 |
| AC-1021 | ACT02635 | AD-4833 |
| AK-56326 | AKOS015894953 | AKOS022109420 |
| API0009130 | Actos | Actos (TN) |
| BBL029068 | BCP26474 | BDBM50103521 |
| BRD-A48430263-003-02-4 | BRD-A48430263-003-06-5 | BSPBio_002723 |
| C07675 | C19H20N2O3S | CCG-220107 |
| CHEBI:8228 | CS-1700 | CTK5B5876 |
| D08378 | DB-027350 | DB01132 |
| DTXSID3037129 | Duetact | FT-0601906 |
| FT-0645030 | GTPL2694 | Glustin |
| HMS2089H14 | HMS3651D09 | HMS3712E16 |
| HS-0047 | HSDB 7322 | HY-13956 |
| HYAFETHFCAUJAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | J-002506 | J-516181 |
| J10289 | K-0703 | KBio2_002103 |
| KBio2_004671 | KBio2_007239 | KBio3_001943 |
| KBioGR_001619 | KBioSS_002103 | KS-00000XMH |
| LS-151327 | MCULE-2346786634 | MLS006011848 |
| NCGC00163128-01 | NCGC00163128-02 | NCGC00163128-03 |
| NCGC00163128-04 | NCGC00163128-05 | NCGC00163128-06 |
| NCGC00163128-07 | NSC-758876 | NSC758876 |
| Pharmakon1600-01504401 | Pioglitazona | Pioglitazona [INN-Spanish] |
| Pioglitazone | Pioglitazone (Actos) | Pioglitazone [BAN:INN] |
| Pioglitazone [INN:BAN] | Pioglitazonum | Pioglitazonum [INN-Latin] |
| Pioglu | Piozone | Q417765 |
| RTX-010718 | SB17323 | SBI-0206791.P001 |
| SC-14147 | SCHEMBL4121 | SMR002204015 |
| SPBio_001897 | SR-01000763737 | SR-01000763737-5 |
| ST24044191 | STL309607 | STL373406 |
| SW197561-3 | Spectrum2_001679 | Spectrum3_001002 |
| Spectrum4_001130 | Spectrum5_001480 | Spectrum5_002067 |
| Spectrum_001623 | U 72107 | U 72107A |
| U-72107 | U72,107A | Zactos |
| [( inverted exclamation markA)-5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl) ethoxy] phenyl] methyl]-2,4-] thiazolidinedione monohydrochlorid | [()-5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl) ethoxy] phenyl] methyl]-2,4-] thiazolidinedione monohydrochlorid | pioglitazone (INN) |
| pioglitazone-actos | s2590 |
| DrugBank Name | Pioglitazone |
| DrugBank | DB01132 |
| CAS Number | 105355-27-9, 105390-47-4, 111025-46-8, 112529-15-4, 1134163-29-3, 1134163-31-7, 627502-58-3, 728045-10-1 |
| PubChem Compound | 4829 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C07675 |
| KEGG Drug | D08378 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46507136 |
| ChEBI | 8228 |
| PharmGKB | PA450970 |
| ChemSpider | 4663 |
| BindingDB | 50103521.0 |
| TTD | DAP000272 |
| Wikipedia | Pioglitazone |
| DPD | 12012 |