D0038 | Diclofenac
S
M
D
S01CC01 Diclofenac and antiinfectives
[S01CC] Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids and antiinfectives in combination
[S01C] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS AND ANTIINFECTIVES IN COMBINATION
[S01] OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
S01BC03 Diclofenac
[S01BC] Antiinflammatory agents, non-steroids
[S01B] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS
[S01] OPHTHALMOLOGICALS
[S] Sensory organs
M02AA15 Diclofenac
[M02AA] Antiinflammatory preparations, non-steroids for topical use
[M02A] TOPICAL PRODUCTS FOR JOINT AND MUSCULAR PAIN
[M02] TOPICAL PRODUCTS FOR JOINT AND MUSCULAR PAIN
[M] Musculoskeletal system
M01AB55 Diclofenac, combinations
[M01AB] Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
[M01A] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS, NON-STEROIDS
[M01] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS
[M] Musculoskeletal system
M01AB05 Diclofenac
[M01AB] Acetic acid derivatives and related substances
[M01A] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS, NON-STEROIDS
[M01] ANTIINFLAMMATORY AND ANTIRHEUMATIC PRODUCTS
[M] Musculoskeletal system
D11AX18 Diclofenac
[D11AX] Other dermatologicals
[D11A] OTHER DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[D11] OTHER DERMATOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS
[D] Dermatological drugs
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 487 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester (TMRE) | decrease | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| PERMEABILIZATION | 12.5 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of MPT | increase | not mentioned | 6 |
| PERMEABILIZATION | 25 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of MPT | increase | not mentioned | 6 |
| PERMEABILIZATION | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of MPT | increase | not mentioned | 6 |
| PERMEABILIZATION | 100 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of MPT | increase | not mentioned | 6 |
| UNCOUPLING | increase | 39 | ||||||
| UNCOUPLING | rat | heart | 197 | |||||
| UNCOUPLING | 197 | |||||||
| PROTONOPHORIC UNCOUPLING | 278 | |||||||
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 50 μmol/L | 3 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential; incubated in the presence of Ca2+ | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 50 μmol/L | 3 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential; incubated in the absence of Ca2+ | Negative | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 250 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 500 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 137.9 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 9.1 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | 29.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| STATE 2 RESPIRATION | 56.3 ± 4.9 | rat | isolated rat liver mitochondria | State 2 respiration ( 96-well plate format using a phosphorescent oxygen-sensitive probe MitoXpress) | inhibit | UC50 (nmol/mg mitochondrial protein) | 40 | |
| STATE 3 RESPIRATION | 100 nmol/mg mitochondrial protein | rat | isolated rat liver mitochondria | State 3 respiration ( 96-well plate format using a phosphorescent oxygen-sensitive probe MitoXpress) | Negative | IC50 (nmol/mg mitochondrial protein) | 40 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex I activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex IV activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex V activity | decrease | p < 0.01 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | decrease | 39 | ||||||
| LIPID METABOLISM | 122 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | LipidTox, for neutral lipid accumulation, to evaluate lipid content. | accumulation | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| MITOCHONDRIAL FATTY ACID BETA OXIDATION | 47μM | 11* | mice | Lean mice vs Ob/ob mice | Measurement of oxygen consumption in the presence of ADP (state 3) and the different substrates was carried out on the Mitologics screening platform | EC20 | 227 | |
| ACCUMULATION OF CALCIUM | 50 μmol/L | 2 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assessment of Mitochondrial Ca2+ Efflux; Energized with succinate | decrease | not mentioned | 6 |
| ATP SYNTHESIS | 250 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assay of Cellular ATP contents; Assay of LDH leakage | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| ATP SYNTHESIS | 500 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assay of Cellular ATP contents; Assay of LDH leakage | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| NADPH METABOLISM | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Measurement of Mitochondrial NADPH; incubated in the presence of Ca2+ | increase | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| NADPH METABOLISM | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Measurement of Mitochondrial NADPH; incubated in the absence of Ca2+ | Negative | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| THIOL COMPOUNDS METABOLISM | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assay of Mitochondrial Protein Thiol; Assay of Mitochondrial GSH; incubated in the presence of Ca2+ | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| THIOL COMPOUNDS METABOLISM | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assay of Mitochondrial Protein Thiol; Assay of Mitochondrial GSH; incubated in the absence of Ca2+ | Negative | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| GLUTATHIONE METABOLISM | 167 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | glutathion depletion: cells were incubated with 50 μM monochlorobimane with 6 μg/ml Hoechst 33342 | AC50 (μM) | 40 | |
| SWELLING | > 800 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| ROS PRODUCTION | NR | rat | hepatocytes | use CM-H2DCFDA to monitor reactive oxygen species | Negative | AC50 (μM) | 40 | |
| CYTOCHROME C RELEASE | 197 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | cytochrome c release (anti-cytochrome c antibody ) | induce | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| ER STRESS-INDUCED | 51 | 24hr | rat | hepatocytes | DNA damage 153 induction (GADD153 antibodies) for ER-stress induced apoptosis | induce | AC50 (μM) | 40 |
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex I activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | inhibitor | 39 | ||||||
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 9.1 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | 29.8 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| Cytochrome c oxidase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex IV activity | Negative | p < 0.05 | 3 | |
| ATP synthase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex V activity | inhibitor | p < 0.01 | 3 | |
| ATP | 250 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assay of Cellular ATP contents; Assay of LDH leakage | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| ATP | 500 μmol/L | 24 hours | rat | hepatocytes | Assay of Cellular ATP contents; Assay of LDH leakage | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Thiol compounds | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assay of Mitochondrial Protein Thiol; Assay of Mitochondrial GSH; incubated in the presence of Ca2+ | decrease | p < 0.01 | 6 |
| Thiol compounds | 50 μmol/L | 10 minutes | rat | liver mitochondria | Assay of Mitochondrial Protein Thiol; Assay of Mitochondrial GSH; incubated in the absence of Ca2+ | Negative | p < 0.05 | 6 |
| Cytochrome c | > 200 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
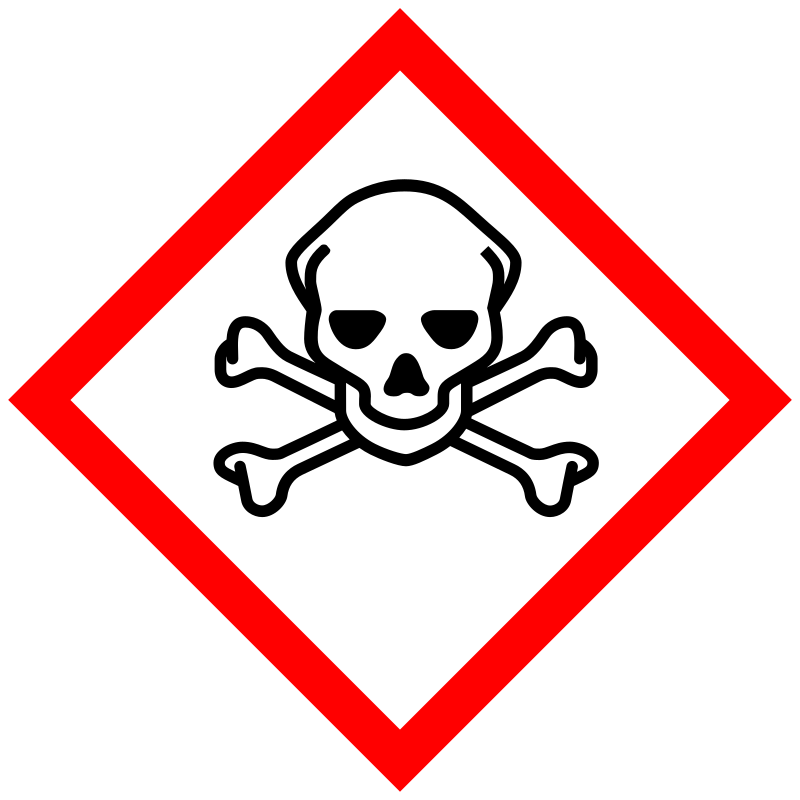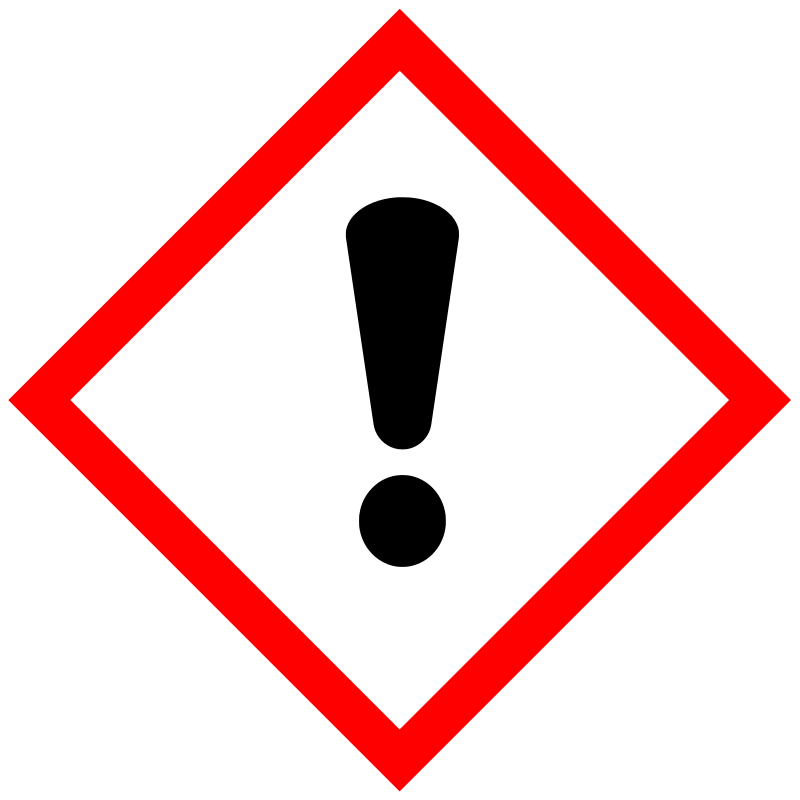  |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 62 companies from 11 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 1 of 62 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 10 notification(s) provided by 61 of 62 companies with hazard statement code(s): H301 (100%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H311 (90.16%): Toxic in contact with skin [Danger Acute toxicity, dermal] H315 (88.52%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H319 (88.52%): Causes serious eye irritation [Warning Serious eye damage/eye irritation] H335 (88.52%): May cause respiratory irritation [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure Respiratory tract irritation] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P361, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
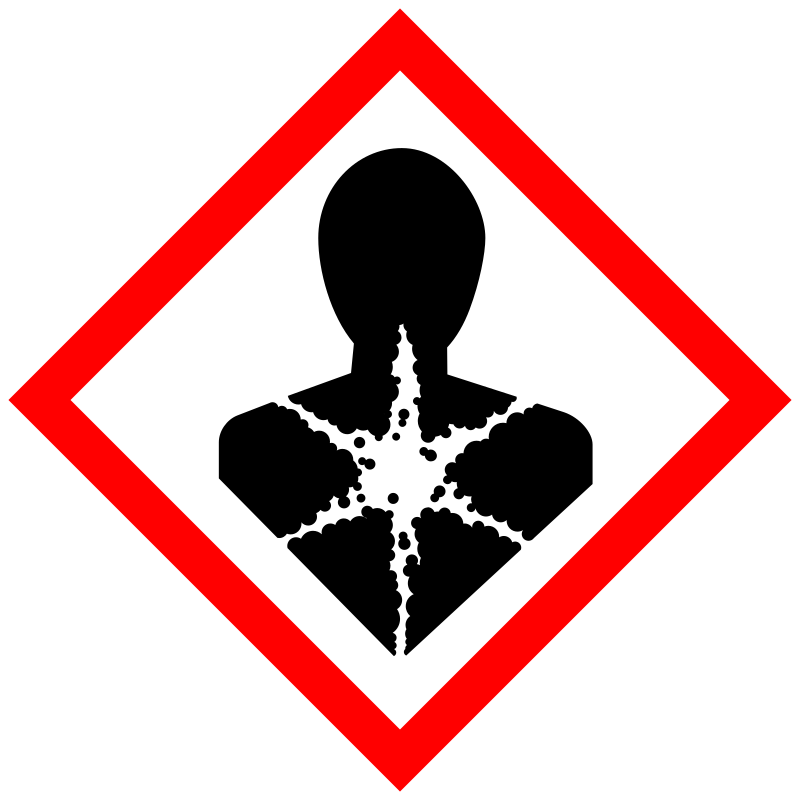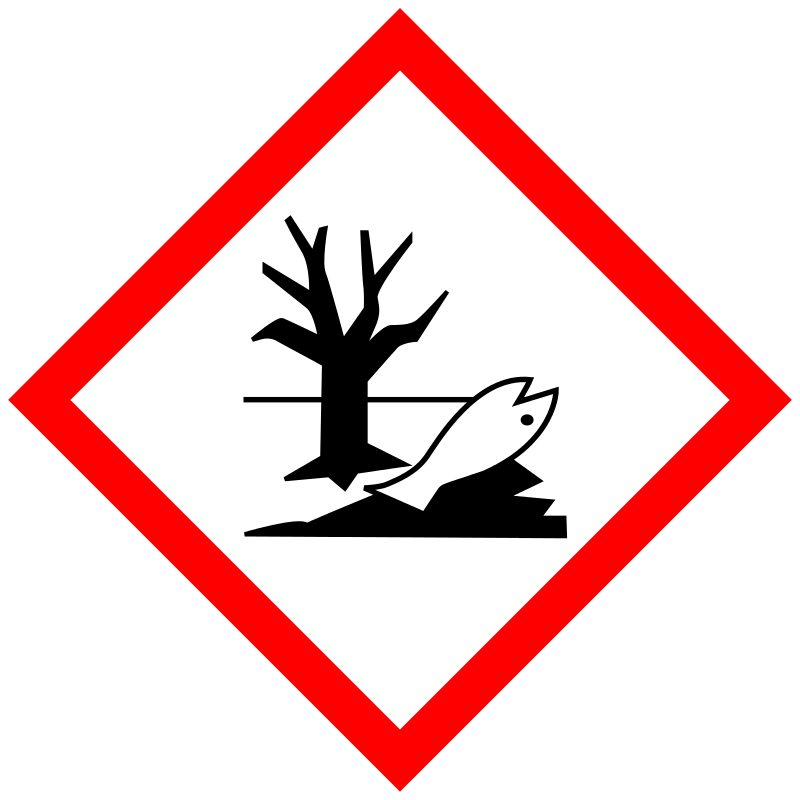    |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 294 companies from 12 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 52 of 294 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 11 notification(s) provided by 242 of 294 companies with hazard statement code(s): H301 (16.12%): Toxic if swallowed [Danger Acute toxicity, oral] H302 (83.88%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H361 (73.55%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H372 (68.18%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H411 (82.64%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P273, P281, P301+P310, P301+P312, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P391, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| man | TDLo | intramuscular | 1070ug/kg (1.07mg/kg) | skin and appendages (skin): "dermatitis, other: after systemic exposure" | Annals of Internal Medicine. Vol. 117, Pg. 1058, 1992. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 345mg/kg (345mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 43, Pg. 44, 1993. | |
| man | TDLo | oral | 29mg/kg (29mg/kg) | blood: "changes in serum composition (e.g., tp, bilirubin, cholesterol)" | Journal of Toxicology, Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 33, Pg. 173, 1995. |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 170mg/kg (170mg/kg) | Pharmazie. Vol. 37, Pg. 148, 1982. | |
| rat | LD50 | oral | 62500ug/kg (62.5mg/kg) | Arzneimittel-Forschung. Drug Research. Vol. 30, Pg. 1398, 1980. | |
| (2-((2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino-phenyl)acetic acid (HD) | 056D694 | 144O8QL0L1 |
| 15307-86-5 | 2-((2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino)benzeneacetic acid | 2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenylacetic Acid |
| 2-(2-((2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino)phenyl)acetic acid | 2-(2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)phenyl)acetic acid | 2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]benzeneacetic acid |
| 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-amino]-benzeneacetic acid | 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-amino]-phenyl-acetic acid | 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-benzeneacetic acid |
| 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-phenyl-acetic acid | 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenylacetic acid | 2-[2,6-DICHLOROPHENYL)AMINO]BENZENEACETIC ACID |
| 2-[2-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)aminophenyl]ethanoic acid | 2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid | 2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid. |
| 2-[2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)aminophenyl]ethanoic acid | 2-[2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-phenyl]-acetic acid | 2-[2-(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)phenyl]-acetic acid |
| 2-[2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl]acetic Acid (Diclofenac) | 2-[2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl]acetic acid | 2-{2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid |
| 2b17 | AB01275502-01 | AB01275502_02 |
| AB1009343 | AC-27673 | ACETIC ACID, (o-(2,6-DICHLOROANILINO)PHENYL)- |
| ACMC-209d8r | AK-75694 | AKOS001579542 |
| ANW-21433 | Arthrotec | BCP09087 |
| BCP13860 | BDBM13066 | BIDD:GT0380 |
| BPBio1_000516 | BRD-K08252256-236-05-6 | BRD-K08252256-236-17-1 |
| BRN 2146636 | BSPBio_000468 | BSPBio_002169 |
| Benzeneacetic acid, 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)- | Benzeneacetic acid, 2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino)- (9CI) | Benzeneacetic acid, 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]- |
| C01690 | CHEBI:47381 | CHEMBL139 |
| CS-2862 | CTK8B0851 | D07816 |
| D3748 | DB00586 | DCOPUUMXTXDBNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| DIF | DTXSID6022923 | Dichlofenal |
| Diclofenac (USAN/INN) | Diclofenac [INN:BAN] | Diclofenac [USAN:INN:BAN] |
| Diclofenac acid | Diclofenac resinate | Diclofenaco |
| Diclofenaco [INN-Spanish] | Diclofenacum | Diclofenacum [INN-Latin] |
| Diclofenamic acid | Diclonate P | Diclophenac |
| Dicrofenac | DivK1c_000272 | DivK1c_000402 |
| EBD50236 | EC 239-348-5 | EINECS 239-348-5 |
| Epitope ID:116873 | F0722-0745 | FT-0624731 |
| GP-45,840 | GP-45840 | GTPL2714 |
| HMS2090C10 | HMS501E04 | HSDB 7234 |
| HY-15036 | IDI1_000272 | IDI1_000402 |
| ISV-205 | KBio1_000272 | KBio1_000402 |
| KBio2_001410 | KBio2_002306 | KBio2_003978 |
| KBio2_004874 | KBio2_006546 | KBio2_007442 |
| KBio3_001389 | KBio3_002786 | KBioGR_001051 |
| KBioGR_002306 | KBioSS_001410 | KBioSS_002308 |
| KS-000001OB | KS-1258 | LS-11575 |
| Lopac0_000441 | M-7482 | MCULE-1824024270 |
| MLS006011795 | NCGC00021125-01 | NCGC00021125-02 |
| NINDS_000272 | NINDS_000402 | Novapirina |
| Olfen | Oprea1_011155 | Pennsaid |
| Prestwick0_000594 | Prestwick1_000594 | Prestwick2_000594 |
| Prestwick3_000594 | ProSorb-D | Q244408 |
| SBI-0051341.P003 | SC-16284 | SCHEMBL2799 |
| SMR001550371 | SPBio_001081 | SPBio_002687 |
| SR-01000003041-3 | SR-38 | ST51039044 |
| STK984493 | Solaraze | Solaraze (TN) |
| Spectrum2_000991 | Spectrum3_000385 | Spectrum4_000506 |
| Spectrum5_000867 | Spectrum_000930 | TC-110178 |
| UNII-144O8QL0L1 | UNM000001216103 | Voltaren |
| Voltaren-XR | Voltarol | Z57664869 |
| ZINC1281 | Zorovolex | Zorvolex |
| Zorvolex (TN) | [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]-acetic acid | [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid |
| [2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetic acid # | [2-(2,6-dichloro-phenylamino)-phenyl]-acetic acid | [o-(2,6-dichloro-anilino)-phenyl]-acetic acid |
| cMAP_000014 | dichlofenac | diclofenac |
| o-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenylacetic acid | {2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid |
| DrugBank Name | Diclofenac |
| DrugBank | DB00586 |
| CAS Number | 119623-66-4, 128402-48-2, 15307-86-5, 15362-40-0, 23049-93-6, 78213-16-8, 79183-19-0 |
| PubChem Compound | 3033 |
| KEGG Compound ID | C01690 |
| KEGG Drug | D07816 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46504644 |
| ChEBI | 47381 |
| PharmGKB | PA449293 |
| ChemSpider | 2925 |
| BindingDB | 13066.0 |
| TTD | DAP000620 |
| Wikipedia | Diclofenac |
| HET | DIF |
| DPD | 2013|1205|20061 |